国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 26-33.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2024.02.004
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue CAO1,2,3( ),Weimiao QIAN1,2,3,*(
),Weimiao QIAN1,2,3,*( ),Guocui LI3,Yang FENG3,Tong GAO3
),Guocui LI3,Yang FENG3,Tong GAO3
Received:2022-09-04
Online:2024-04-28
Published:2024-05-25
Contact:
Weimiao QIAN
E-mail:c_yue93@yeah.net;qianweimiao@163.com
CLC Number:
Yue CAO,Weimiao QIAN,Guocui LI,Yang FENG,Tong GAO. Characteristics of fine-scale distribution of short-term heavy precipitation over the central and southern regions of Hebei province in summers from 2013 to 2020[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 26-33.
Fig.6
Diurnal variation of the number of stations with different hourly precipitation intensity of HHR (a), the number of stations within different precipitation intensity intervals (b), and the average hourly precipitation intensity (c) in the central and southern regions of Hebei province in summers from 2013 to 2020"
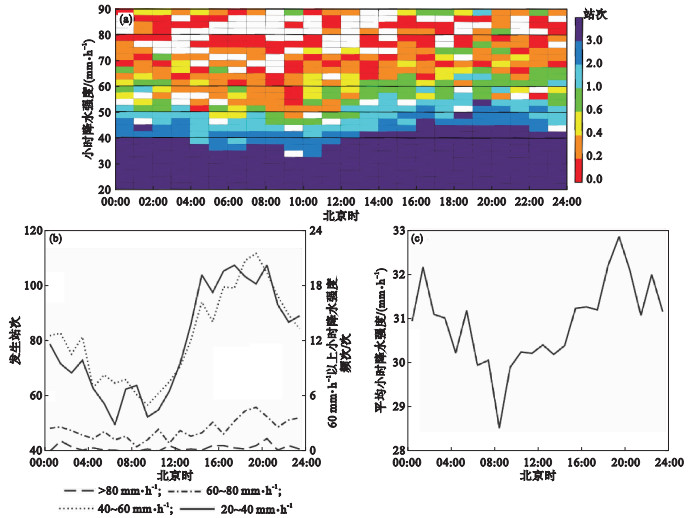
Table 2
Annual occurrence frequency of HHR over its high-frequency areas in the central and southern regions of Hebei province in summers from 2013 to 2020 次"
| 区域 | 2013年 | 2014年 | 2015年 | 2016年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 平均/(次/a) |
| 西部山区 | 10 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 13 | 19 | 9 | 17 | 14.1 |
| 东部沿海 | 15 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 16 | 11 | 13 | 12 | 12.9 |
| 保定中部 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3.4 |
| 区域性 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 5.9 |
| 1 |
Zhang H , Zhai P M . Temporal and spatial characteristics of extreme hourly precipitation over eastern China in the warm season[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 28, 1177- 1183.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-011-0020-0 |
| 2 |
Luo Y L , Wu M W , Ren F M , et al. Synoptic situations of extreme hourly precipitation over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2016, 29 (24): 8703- 8719.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0057.1 |
| 3 | 孙继松. 短时强降水和暴雨的区别与联系[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36 (6): 498- 506. |
| 4 | 孙继松, 何娜, 王国荣, 等. "7·21"北京大暴雨系统的结构演变特征及成因初探[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2012, 31 (3): 218- 225. |
| 5 | 张迎新, 李宗涛, 姚学祥. 京津冀"7·21"暴雨过程的中尺度分析[J]. 高原气象, 2015, 34 (1): 202- 209. |
| 6 | 孟丹, 宫辉力, 李小娟, 等. 北京7·21暴雨时空分布特征及热岛—雨岛响应关系[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2017, 29 (1): 178- 185. |
| 7 | 孙玉龙, 张素云, 赵铁松, 等. 河北省"7·19"特大暴雨灾害评估和分析[J]. 中国水利, 2018, (3): 44- 45. |
| 8 |
Xia R D , Zhang D L . An observational analysis of three extreme rainfall episodes of 19-20 July 2016 along the Taihang Mountains in North China[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2019, 147 (11): 4199- 4220.
doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-18-0402.1 |
| 9 | 张霞, 杨慧, 王新敏, 等. "21·7"河南极端强降水特征及环流异常性分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44 (5): 672- 687. |
| 10 | 史文茹, 李昕, 曾明剑, 等. "7·20"郑州特大暴雨的多模式对比及高分辨率区域模式预报分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44 (5): 688- 702. |
| 11 | 田付友, 郑永光, 张涛, 等. 我国中东部不同级别短时强降水天气的环境物理量分布特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36 (6): 518- 526. |
| 12 | 吴梦雯, 罗亚丽. 中国极端小时降水2010—2019年研究进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38 (5): 502- 514. |
| 13 | 刘伟东, 尤焕苓, 任国玉, 等. 北京地区自动站降水特征的聚类分析[J]. 气象, 2014, 40 (7): 844- 851. |
| 14 | 花家嘉, 张婉莹, 陈桂万, 等. 河北唐山地区盛汛期短时强降水概念模型及物理量特征分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2016, 38 (2): 463- 472. |
| 15 |
Li H Q , Cui X P , Zhang D L . A statistical analysis of hourly heavy rainfall events over the Beijing metropolitan region during the warm seasons of 2007-2014[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2017, 37 (11): 4027- 4042.
doi: 10.1002/joc.4983 |
| 16 | 傅佩玲, 胡东明, 张羽, 等. 2017年5月7日广州特大暴雨微物理特征及其触发维持机制分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44 (4): 500- 510. |
| 17 | 杨晓亮, 杨敏, 段宇辉, 等. 京津冀一次暖区大暴雨的成因分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40 (5): 455- 465. |
| 18 | 王国荣, 王令. 北京地区夏季短时强降水时空分布特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2013, 32 (3): 276- 279. |
| 19 | 王婧羽, 李哲, 汪小康, 等. 河南省雨季短时强降水时空分布特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38 (2): 152- 160. |
| 20 | 高留喜, 李静, 刘畅, 等. 山东省短时极端强降水研究[J]. 气象科技, 2014, 42 (3): 482- 487. |
| 21 |
童金, 魏凌翔, 叶金印, 等. 安徽省不同地形条件下汛期短时强降水时空分布特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2017, 33 (6): 42- 48.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2017.06.006 |
| 22 | 冷亮, 周伶俐, 肖艳姣, 等. 基于地面分钟雨量数据的湖北省短时强降水时空分布特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40 (1): 61- 68. |
| 23 | 沈澄, 颜廷柏, 刘冬晴, 等. 2008—2012年南京短时强降水特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2015, 31 (1): 28- 33. |
| 24 | 《河北省天气预报手册》编写组. 河北省天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2017: 6. |
| 25 | 高霞, 王宏, 于成文, 等. 近45年来河北省极端降水事件的变化研究[J]. 气象, 2009, 35 (7): 10- 15. |
| 26 | 刘金平, 韩军彩, 向亮, 等. 1961—2012年京津冀地区不同等级降水日数时空演变特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2015, 31 (1): 43- 50. |
| 27 | 申莉莉, 张迎新, 隆璘雪, 等. 1981—2016年京津冀地区极端降水特征研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2018, 37 (5): 428- 434. |
| 28 | 岳艳霞, 陈静, 郭志斌. 区域自动站雨量资料质量控制方法及应用[J]. 气象科技, 2009, 37 (4): 452-456, 后插6. |
| 29 | 任芝花, 赵平, 张强, 等. 适用于全国自动站小时降水资料的质量控制方法[J]. 气象, 2010, 36 (7): 123- 132. |
| 30 | 任芝花, 张志富, 孙超, 等. 全国自动气象站实时观测资料三级质量控制系统研制[J]. 气象, 2015, 41 (10): 1268- 1277. |
| 31 | 王丛梅, 俞小鼎, 刘瑾, 等. 弱天气尺度背景下太行山极端短时强降水预报失败案例剖析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44 (1): 107- 117. |
| 32 | 孙密娜, 韩婷婷, 王艳春. 北上台风"安比"强降水落区变化特征及其成因[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38 (4): 569- 580. |
| 33 | 高拴柱. 2018年台风温比亚的强对流螺旋雨带观测特征分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46 (6): 792- 800. |
| 34 | 何立富, 陈双, 郭云谦. 台风利奇马(1909)极端强降雨观测特征及成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31 (5): 513- 526. |
| [1] | Dongnan LI,Qiannan GAO,Guozhi SUN,Pengfei SUN,Ximing ZHANG,Qiang XIA. Spatiotemporal distribution of precipitation in Heilongjiang province from 1991 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 17-25. |
| [2] | DAI Zhu-jun, WU Hai-ying, JIANG You-shan, XIA Min-jie, ZHU Xin-jun, QING Tao. Characteristics of water vapor transport in precipitation difference between two landing typhoons of “Jelawat” and “Haiku” [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(5): 16-24. |
| [3] | AN Lin-chang, ZHANG Heng-de, LI Kai-fei. Analysis of effect of precipitation events on air pollutant concentration [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(3): 58-70. |
| [4] | WANG Xiu-ping, WANG Shuo, LI Xiao-xiao. Analysis of precipitation trend in Dalian from 1971 to 2013 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(3): 47-52. |
| [5] | CHENG Hang,CHENG Xiang-kun,ZHU Jing,LI Hong-qiang,LIU Xiao-chu. Application of precipitable water vapor from ground based GPS to three precipitation processes in Dalian region [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(5): 38-48. |
| [6] | ZHAO Hu-jia,MA Yan-jun,ZHU Yi-ming,GAO Qing-yuan. Characteristics of visibility over Anshan from 2010 to 2011 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(1): 18-22. |
| [7] | HU Peng,HU Ming-bao,ZHANG Cheng-cheng,YANG Jin-wei. A primary analysis of different algorithms of KDP based on S band dual-polarization Doppler radar [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2012, 28(1): 77-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|