国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2020, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 31-41.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2020.06.004
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ping JIANG1,2( ),Xiao-ran LIU1,*(
),Xiao-ran LIU1,*( ),Jun KANG1,Dai-qiang LIAO1,Jie ZHOU1
),Jun KANG1,Dai-qiang LIAO1,Jie ZHOU1
Received:2019-11-01
Online:2020-12-30
Published:2021-01-06
Contact:
Xiao-ran LIU
E-mail:995879751@163.com;liuxiaoran8283@126.com
CLC Number:
Ping JIANG,Xiao-ran LIU,Jun KANG,Dai-qiang LIAO,Jie ZHOU. Quantitative assessment of wind environment in neighborhoods based on exceeding probability in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 31-41.
Table 6
Frequencies and estimated parameters(βi and ηi)of Weibull distribution in each wind direction i at Shapingba station in Chongqing from 2004 to 2018"
| 参数 | N | NNE | NE | ENE | E | ESE | SE | SSE | S | SSW | SW | WSW | W | WNW | NW | NNW | |
| 风向频率pi/(%) | 5.32 | 2.98 | 4.12 | 4.64 | 3.55 | 3.48 | 3.72 | 2.39 | 2.22 | 3.27 | 2.70 | 2.41 | 8.43 | 22.51 | 18.37 | 9.79 | |
| 威布尔分布参数 | βi | 2.23 | 2.83 | 2.88 | 2.85 | 2.73 | 2.69 | 2.62 | 2.43 | 2.54 | 2.78 | 2.77 | 2.65 | 3.17 | 3.52 | 2.92 | 2.51 |
| ηi | 1.56 | 1.21 | 1.31 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.53 | 1.64 | 1.52 | 1.40 | 1.47 | 1.25 | 1.15 | 1.42 | 1.59 | 1.76 | 1.84 |
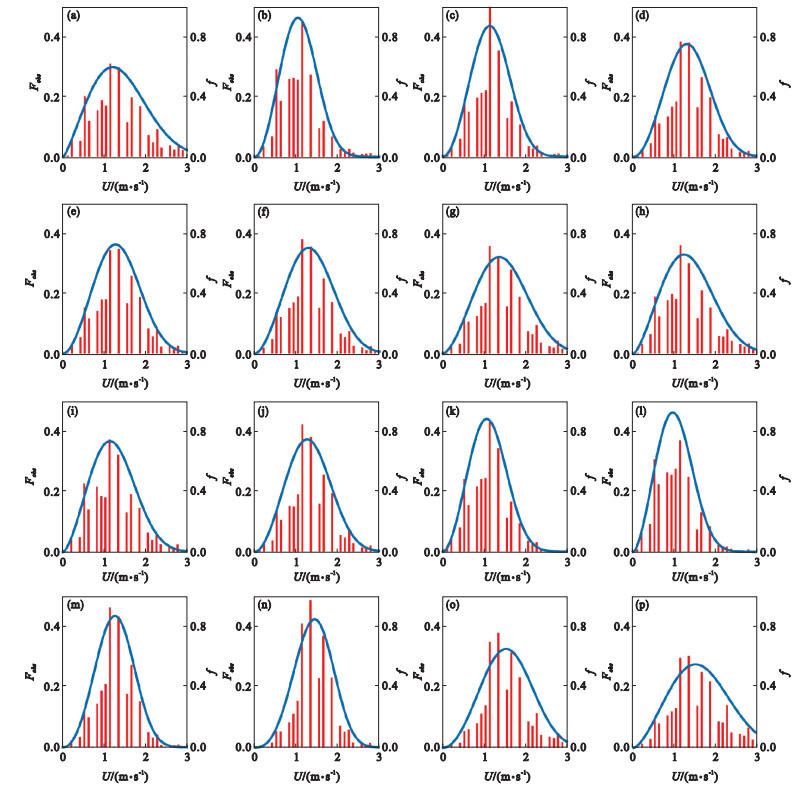
Fig.4
Observed probability distribution of wind speed(Fobs, red bars)and fitting probability density of Weibull distribution in wind direction of N (a), NNE (b), NE (c), ENE (d), E (e), ESE (f), SE (g), SSE (h), S (i), SSW (j), SW (k), WSW (l), W (m), WNW (n), W (o) and NNW (p) at Shapingba station in Chongqing from 2004 to 2018"
| 1 |
胡非, 洪钟祥, 雷孝恩. 大气边界层和大气环境研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 2003, 27 (4): 712- 728.
doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2003.04.18 |
| 2 |
金琪, 孟英杰. 1960-2016年武汉城市圈人体舒适度变化特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2017, 33 (6): 82- 88.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2017.06.011 |
| 3 | 赵会兵, 江源通, 郑拴宁. 城市形态对城市风环境品质影响的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39 (S2): 59- 65. |
| 4 | 杨栋, 朱佳敏, 姚日升, 等. 宁波地区空气质量及大气自净能力海陆差异对比[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2019, 35 (3): 52- 59. |
| 5 | 赵蕾, 吴坤悌, 陈明. 2013-2016年海口市空气质量特征及典型个例污染物来源分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2019, 35 (5): 63- 69. |
| 6 | 冯章献, 王士君, 金珊合, 等. 长春市城市形态及风环境对地表温度的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74 (5): 902- 911. |
| 7 | Aynsley R M . Politics of pedestrian level urban wind control[J]. Building and Environment, 1989, 24 (4): 291- 295. |
| 8 |
蒙伟光, 闫敬华, 扈海波. 城市化对珠江三角洲强雷暴天气的可能影响[J]. 大气科学, 2007, 31 (2): 364- 376.
doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.02.17 |
| 9 | Mittal H , Sharma A , Gairola A . A review on the study of urban wind at the pedestrian level around buildings[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2018, (18): 154- 163. |
| 10 | Oke T R . The energetic basis of the urban heat island[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1982, 108 (455): 1- 24. |
| 11 | 蒋维楣, 苗世光, 张宁, 等. 城市气象与边界层数值模拟研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2010, 25 (5): 463- 473. |
| 12 | 刘辉志, 姜瑜君, 梁彬, 等. 城市高大建筑群周围风环境研究[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2005, 35 (Z1): 84- 96. |
| 13 |
Miao Y C , Liu S H , Chen B C , et al. Simulating urban flow and dispersion in Beijing by coupling a CFD model with the WRF model[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 30 (6): 1663- 1678.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2234-9 |
| 14 |
Inagaki A , Castillo M C L , Yamashita Y , et al. Large-eddy simulation of coherent flow structures within a cubical canopy[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2012, 142 (2): 207- 222.
doi: 10.1007/s10546-011-9671-8 |
| 15 | Murakami S , Iwasa Y , Morikawa Y . Study on acceptable criteria for assessing wind environment at ground level based on residents' diaries[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1986, 24 (1): 1- 18. |
| 16 | White B R . Analysis and wind-tunnel simulation of pedestrian-level winds in San Francisco[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1992, 44 (1/2/3): 2353- 2364. |
| 17 | 李磊, 胡非, 刘京. CFD技术在我国城市气候环境微尺度问题中的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2015, 5 (6): 23- 30. |
| 18 | Davenport A G.An approach to human comfort criteria for environmental wind conditions[C]//Colloquium on Building Climatology.Sweden, Stockholm: Swedish National Buiding Research Institute, 1972. |
| 19 | Soligo M J , Irwin P A , Williams C J , et al. A comprehensive assessment of pedestrian comfort including thermal effects[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1998, s98 (77/78): 753- 766. |
| 20 | Penwarden A D . Acceptable wind speeds in towns[J]. Building Science, 1973, 8 (3): 259- 267. |
| 21 | To A P , Lam K M . Evaluation of pedestrian-level wind environment around a row of tall buildings using a quartile-level wind speed descripter[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1995, 54 (94): 527- 541. |
| 22 | Mochida A , Lun I Y F . Prediction of wind environment and thermal comfort at pedestrian level in urban area[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96 (10/11): 1498- 1527. |
| 23 | 杨易, 金新阳, 金海, 等. 新广州火车站风环境数值模拟研究与评估[J]. 建筑科学, 2010, 26 (3): 53- 57. |
| 24 | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.绿色建筑评价标准(GB/T 50378-2014)[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. |
| 25 | Melbourne W H . Criteria for environmental wind conditions[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1978, 3 (2/3): 241- 249. |
| 26 | Sha W . Design of the dynamics core for a new-generation numerical model of the local meteorology[J]. Kaiyo Monthly, 2002, 34 (2): 107- 112. |
| 27 | Sha W . Local meteorological model based on LES over the Cartesian coordinate and complex surface[M]. Tokyo: Meteorological Society of Japan Press, 2008: 21- 26. |
| 28 | 金良琼.两参数Weibull分布的参数估计[D].昆明: 云南大学, 2010. |
| 29 | 蒋仁言, 左明建. 可靠性模型与应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1999. |
| [1] | LI Shuang, DING Zhi-ying, ZHAO Huan, XING Rui, KANG Xiao-yu, HAN Yan-feng. Analysis of multi-scale characteristics of a short-time rainstorm process in Liaoning province in 2014 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(6): 75-83. |
| [2] | WU Chang-guang, FANG Ya-ping, LIN Yao-yu, MA Xiao-yang, WANG Yao-wu, WANG Ke-huan. Analysis of the effect of street greenbelt on microclimate in a hot-humid area of China using a numerical simulation method [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(5): 99-106. |
| [3] | AI Kai, ZHENG Yi-qun, ZENG Xin-min, CHEN Hao-wei. Effect of different cloud microphysical parameterization schemes of WRF model on autumn precipitation over West China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(2): 1-10. |
| [4] | JIANG Yang, HE Zhi-xin, ZHOU Kun, ZHU Hong-fang, WANG Dong-yong. Analysis of forming reason of freezing rain weather and its characteristics in mountain and plain of Anhui province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(2): 11-17. |
| [5] | ZOU Xu-dong,YANG Hong-bin,ZHANG Yun-hai,LIU Yu-che,WANG Hong-yu. Numerical simulation of haze weather in the central cities of Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(6): 92-99. |
| [6] | ZHANG Nan,YI Xiao-yuan,ZHU Li-juan,WANG Qing-yuan. Analysis of two heavy snow/rain processes influenced by surface cyclone in North China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(5): 7-14. |
| [7] | WANG Kai-yan,DENG Tao, DENG Xue-jiao,LI Hai-yang,ZHAO Xiao-wei,QI Xiu-xiang. Numerical simulation analysis of a haze numerical forecast system in process of different synoptic types [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(5): 21-26. |
| [8] | WANG Jing,ZHAO Yu-jie,WU Zhen-ling,CAI Zi-ying . Effects of establishment of mixed layer on a strong gust weather process [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(4): 26-33. |
| [9] | CHENG Xiang-kun, CHENG Hang,XU Jie,MA Yan-jun. A numerical simulation test of a sea fog event over the Yellow Sea [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(6): 15-23. |
| [10] | XIE Jin-fan ,WANG Yu-kun ,ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Ting ,YU Li. The application of numerical simulation technique to macro-siting of wind farm [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(5): 148-153. |
| [11] | SONG Xiao-hui,TIAN Li-qing,TIAN Xiu-xia,MA Hong-qing,ZHANG Gong-wen,DONG Fang-liang. Numerical simulation on a return-flow snowstorm process in Hebei province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(3): 8-14. |
| [12] | WANG Wen,CHENG Pan. Numerical simulation and diagnostic analysis of a rainstorm process [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(1): 1-11. |
| [13] | ZOU Xu-dong,YANG Hong-bin,LI Shuai-bin,LIU Yu-che,WANG Hong-yu. Numerical simulation for a pollution weather process in Shengyang, Liaoning province using MM5 model and NCEP/NCAR data [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2012, 28(4): 8-15. |
| [14] | ZOU Xu-Dong, TIAN Xiao-Bo, YANG Hong-Bin, WANG Hong-Yu, LIU Yu-Che, ZHANG Yun-Hai. Simulation analysis of PM10 emission from typically atmospheric pollution sources in winter of 2007 over Shenyang [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2011, 27(6): 28-34. |
| [15] | YANG Xiao-jun,;HE Jin-hai;Lv Jiang-jin;ZHU Lei-lei;HE Qun-ying;WANG Ying. Numerical simulation on storm surge caused by extratropical cyclone in Bohai Sea, China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2010, 26(4): 61-65. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|