国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 86-95.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2024.02.011
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tao ZUO1,2( ),Ke WANG1,2,Xiaolei SUN1,2,Yanan WANG1,2
),Ke WANG1,2,Xiaolei SUN1,2,Yanan WANG1,2
Received:2022-09-11
Online:2024-04-28
Published:2024-05-25
CLC Number:
Tao ZUO,Ke WANG,Xiaolei SUN,Yanan WANG. Spatiotemporal distribution of thunderstorm gust in the central and western Bohai Sea from 2018 to 2021[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 86-95.
Fig.3
Histogram of occurrence time of thunderstorm gust events (a), the initiation time (b) and the end time (c) of widespread thunderstorm gust events, and the duration of both thunderstorm gust events and widespread thunderstorm gust events (d) in the central and western Bohai Sea from April to September during 2018-2021"
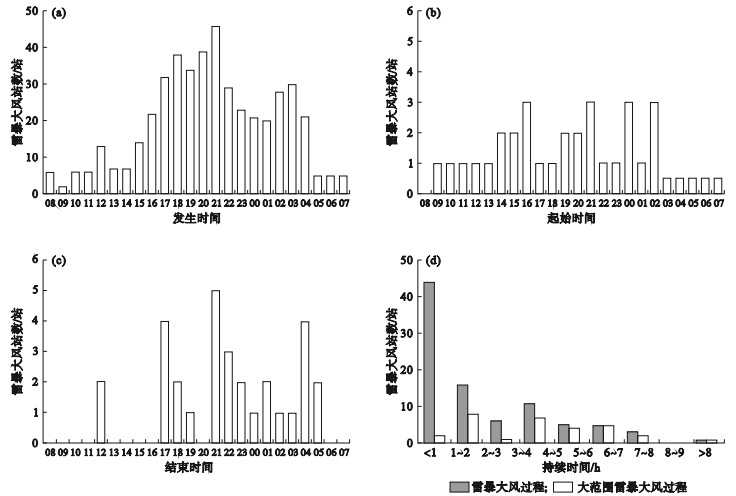
Fig.12
Boxplots of monthly variation of the difference between temperature and dew-point temperature at 500 hPa during widespread thunderstorm gust events (a) and that under different synoptic pattern types (b), the difference between temperature and dew-point temperature at 850 hPa during widespread thunderstorm gust events (c) and that under different synoptic pattern types (d) in the central and western Bohai Sea from May to August during 2018-2021"
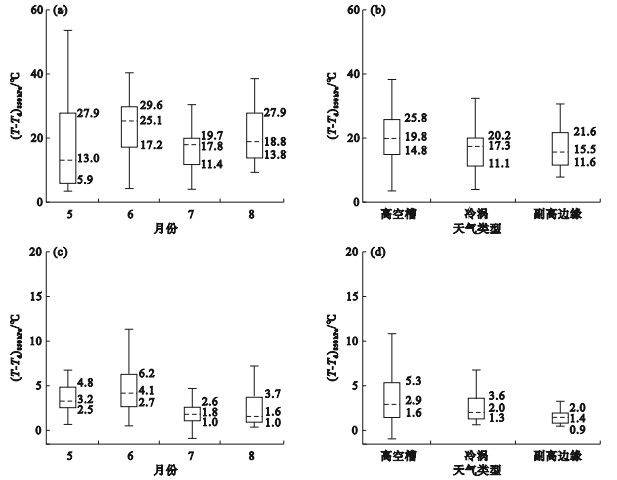
Table 1
Reference threshold values of physical parameters within 0~6 h before widespread thunderstorm gust events in the central and western Bohai Sea"
| 物理量 | CAPE/(J·kg-1) | K/℃ | LI/℃ | T850-500 hPa/℃ | 0~6 km垂直风切变/(m·s-1) | |
| 逐月 | 5月 | ≥206 | ≥30.7 | ≤-0.2 | ≥30.2 | ≥23.8 |
| 6月 | ≥760 | ≥30.9 | ≤-3.5 | ≥30.3 | ≥25.2 | |
| 7月 | ≥2304 | ≥36.9 | ≤-4.0 | ≥25.6 | ≥13.8 | |
| 8月 | ≥2913 | ≥35.6 | ≤-4.7 | ≥25.5 | ≥13.3 | |
| 天气型 | 高空槽 | ≥709 | ≥32.5 | ≤-3.6 | ≥30.2 | ≥15.9 |
| 冷涡 | ≥1130 | ≥34.7 | ≤-2.0 | ≥28.2 | ≥16.1 | |
| 副高边缘 | ≥2764 | ≥38.9 | ≤-4.5 | ≥25.0 | ≥12.2 | |
| 1 |
Johns R H , Doswell Ⅲ C A . Severe local storms forecasting[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 1992, 7 (4): 588- 612.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0434(1992)007<0588:SLSF>2.0.CO;2 |
| 2 | 廖晓农, 于波, 卢丽华. 北京雷暴大风气候特征及短时临近预报方法[J]. 气象, 2009, 35 (9): 19- 28. |
| 3 | 王秀明, 周小刚, 俞小鼎. 雷暴大风环境特征及其对风暴结构影响的对比研究[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71 (5): 839- 852. |
| 4 | 余蓉, 张小玲, 李国平, 等. 1971—2000年我国东部地区雷暴、冰雹、雷暴大风发生频率的变化[J]. 气象, 2012, 38 (10): 1207- 1216. |
| 5 | 费海燕, 王秀明, 周小刚, 等. 中国强雷暴大风的气候特征和环境参数分析[J]. 气象, 2016, 42 (12): 1513- 1521. |
| 6 | 方翀, 王西贵, 盛杰, 等. 华北地区雷暴大风的时空分布及物理量统计特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36 (5): 1368- 1385. |
| 7 | 严仕尧, 李昀英, 齐琳琳, 等. 华北产生雷暴大风的动力热力综合指标分析及应用[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2013, 32 (1): 17- 23. |
| 8 | 俞小鼎, 王秀明, 李万莉, 等. 雷暴与强对流临近预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2020. |
| 9 |
杨晓亮, 杨敏. 2017年秋季河北一次飑线引发的雷暴大风过程分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (6): 1- 9.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2020.06.001 |
| 10 | 秦丽, 李耀东, 高守亭. 北京地区雷暴大风的天气—气候学特征研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2006, 11 (6): 754- 762. |
| 11 | 柴东红, 杨晓亮, 吴紫煜, 等. 京津冀地区雷暴大风天气的统计分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36 (3): 193- 199. |
| 12 | 杨晓霞, 尤莉, 夏凡, 等. 山东内陆和半岛雷暴大风的环境物理量特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2019, 13 (6): 47- 56. |
| 13 | 华雯丽, 杨晓霞, 田雪珊, 等. 山东省雷暴大风天气学分型与物理诊断量统计特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40 (4): 362- 373. |
| 14 | 吕晓娜, 牛淑贞, 张一平, 等. 基于概率与权重的雷暴大风潜势客观预报方法研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2020, 39 (1): 20- 29. |
| 15 | 王彦, 于莉莉, 朱男男, 等. 渤海湾海风锋与雷暴天气[J]. 高原气象, 2011, 30 (1): 245- 251. |
| 16 | 王彦, 唐熠, 赵金霞, 等. 天津地区雷暴大风天气雷达产品特征分析[J]. 气象, 2009, 35 (5): 91-96, 135. |
| 17 |
张晶, 姚文, 陈海涛, 等. 渤海北部东岸海风锋活动及其触发对流特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37 (2): 33- 40.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2021.02.005 |
| 18 | 刘彬贤, 王彦, 刘一玮. 渤海湾海风锋与阵风锋碰撞形成雷暴天气的诊断特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 2015, 38 (1): 132- 136. |
| 19 | 李延江, 景华, 李江波, 等. 一次渤海强对流天气系统监测与大风成因探讨[J]. 海洋预报, 2013, 30 (1): 25- 35. |
| 20 | 王亚男, 李英华, 孙密娜. 下垫面对渤海西部雷雨大风影响的数值模拟分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2019, 36 (3): 24- 32. |
| 21 |
于志明, 王驷鹞, 马东亮. 渤海海洋气象灾害天气分型与预报指标研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2018, 34 (1): 106- 111.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2018.01.013 |
| 22 | 王亚男, 刘一玮, 易笑园. 渤海西部雷雨大风统计特征及对流参数指标分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46 (3): 325- 335. |
| 23 | Taszarek M , Allen J T , Púčik T , et al. Severe convective storms across Europe and the United States. Part Ⅱ: ERA5 environments associated with lightning, large hail, severe wind, and tornadoes[J]. Journal of Climate, 2020, 33 (23): 10263- 10286. |
| 24 | Taszarek M , Pilguj N , Allen J T , et al. Comparison of convective parameters derived from ERA5 and MERRA-2 with rainsonde data over Europe and North America[J]. Journal of Climate, 2021, 34 (8): 3211- 3237. |
| 25 | Taszarek M , Brooks H E , Czernecki B , et al. Climatological aspects of convective parameters over Europe: A comparison of ERA-Interim and sounding data[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31 (11): 4281- 4308. |
| 26 | 孟宪贵, 郭俊建, 韩永清. ERA5再分析数据适用性初步评估[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2018, 38 (1): 91- 99. |
| 27 | 苏永玲, 何立富, 巩远发, 等. 京津冀地区强对流时空分布与天气学特征分析[J]. 气象, 2011, 37 (2): 177- 184. |
| 28 | 高晓梅, 俞小鼎, 王令军, 等. 鲁中地区分类强对流天气环境参量特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2018, 76 (2): 196- 212. |
| 29 | 朱晓彤, 姚凯, 曲美慧, 等. 基于ERA5资料的吉林省东部山区分类强对流预报阈值分析[J]. 气象灾害防御, 2021, 28 (4): 34- 39. |
| 30 | 孙继松, 陶祖钰. 强对流天气分析与预报中的若干基本问题[J]. 气象, 2012, 38 (2): 164- 173. |
| 31 | 俞小鼎, 王秀明, 李万莉, 等. 雷暴与强对流临近预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2020. |
| 32 | Yang X L , Sun J H , Zheng Y G . A 5-yr climatology of severe convective wind events over China[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2017, 32 (4): 1289- 1299. |
| 33 | 王艳, 张义军, 马明. 卫星观测的我国近海海域闪电分布特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21 (2): 157- 163. |
| 34 | 许小峰, 顾建峰, 李永平. 海洋气象灾害[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2009. |
| 35 | 陶局, 易笑园, 赵海坤, 等. 一次飑线过程及其受下垫面影响的数值模拟[J]. 高原气象, 2019, 38 (4): 756- 772. |
| 36 | 杨晓霞, 万明波, 王文青, 等. 山东省雷暴大风天气的气候特征[J]. 山东气象, 2012, 32 (4): 16- 20. |
| 37 | 雷蕾, 孙继松, 魏东. 利用探空资料判别北京地区夏季强对流的天气类别[J]. 气象, 2011, 37 (2): 136- 141. |
| [1] | YANG Lei, WANG Ying, SUN Li, LIU Rui-xia, CAI Kui-zhi, LI Ming-jian. Introduction of LAPS and its application in a rainstorm case in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(6): 1-8. |
| [2] | CHEN Lei, MA Jing-hui, ZHEN Xin-rong, CAO Yu. Variation characteristics and meteorological influencing factors of air pollution in Shanghai [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(3): 59-67. |
| [3] | YAN Fang,CHEN Jing,BIAN Tao,LIAO Ying-hui,ZHANG Cui-hua. Analysis of physical parameter field and echo characteristics of Doppler radar in a thunderstorm process [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(1): 33-39. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|