国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 33-39.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2021.04.005
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-08-07
Online:2021-08-30
Published:2021-09-10
CLC Number:
Min XU. Numerical simulation on the spatiotemporal distribution of PM2.5 in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(4): 33-39.
Fig.3
Variation of simulated and observed hourly mean PM2.5 concentrations at Zhangjiang monitoring station in Pudong District of Shanghai (a), Nanjing olympic sports center monitoring station (b), Hangzhou Xiasha monitoring station (c), and Hefei Changjiang middle road monitoring station (d) in the Yangtze River Delta in 2018"
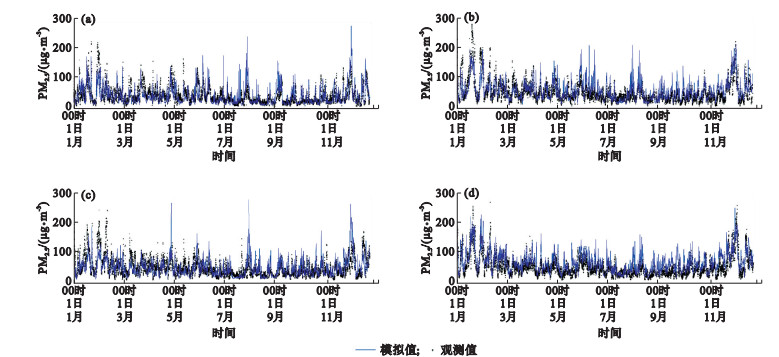
Fig.5
Scatter plots of observed and simulated hourly mean PM2.5 concentration at Zhangjiang monitoring station in Pudong district of Shanghai (a), Nanjing olympic sports center monitoring station (b), Hangzhou Xiasha monitoring station (c), and Hefei Changjiang middle road monitoring station (d) in the Yangtze River Delta of China in 2018"
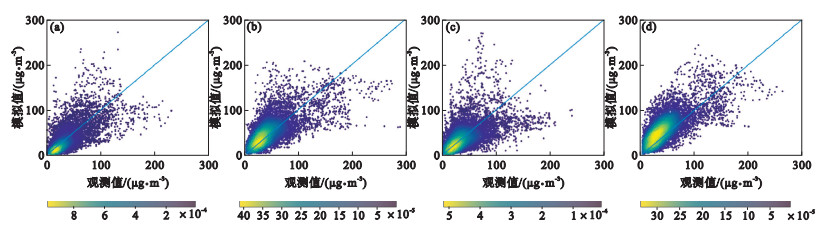
Table 1
Statistical parameters of simulated hourly PM2.5 of the monitoring stations in the Yangtze River Delta of China in 2018"
| 监测站点 | R | MB/(μg·m-3) | NMB/(%) | RMSE/(μg·m-3) | NME/(%) |
| 上海浦东张江 | 0.68 | -2.51 | -6.73 | 24.21 | 43.24 |
| 南京奥体中心 | 0.67 | 4.51 | 9.30 | 28.87 | 41.69 |
| 杭州下沙 | 0.52 | -0.98 | -2.31 | 30.14 | 47.21 |
| 合肥长江中路 | 0.71 | 13.73 | 29.65 | 29.28 | 48.07 |
| 长三角地区所有监测站 | 0.64 | 3.87 | 9.06 | 29.03 | 45.47 |
| 1 |
钟流举, 郑君瑜, 雷国强, 等. 空气质量监测网络发展现状与趋势分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2007, 23 (2): 113- 118.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2007.02.029 |
| 2 |
Pope III C A . Air pollution and health-good news and bad[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2004, 351 (11): 1132- 1133.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMe048182 |
| 3 |
Wang J , Hu Z M , Chen Y Y , et al. Contamination characteristics and possible sources of PM10 and PM2.5 in different functional areas of Shanghai, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 68, 221- 229.
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.10.070 |
| 4 | 李杰, 杨文夷, 陈焕盛, 等. 东亚大气可吸入颗粒物时空分布的数值模拟研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34 (3): 548- 557. |
| 5 |
Timmermans R , Kranenburg R , Manders A , et al. Source apportionment of PM2.5 across China using LOTOS-EUROS[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2017, 164, 370- 386.
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.06.003 |
| 6 | Brasseur G P , Xie Y , Petersen A K , et al. Ensemble forecasts of air quality in eastern China-Part 1:Model description and implementation of the MarcoPolo-Panda prediction system[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2019, 12, 33- 67. |
| 7 |
邹旭东, 田晓波, 杨洪斌, 等. 2007年冬季沈阳典型大气污染源PM10排放模拟[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2011, 27 (6): 28- 34.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2011.06.005 |
| 8 | 王开燕, 邓涛, 邓雪娇, 等. 灰霾数值预报系统对不同天气型过程数值模拟分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2014, 30 (5): 21- 26. |
| 9 | 杨文夷, 李杰, 陈焕盛, 等. 东亚边界层臭氧时空分布的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34 (7): 1633- 1641. |
| 10 | 邹旭东, 杨洪斌, 张云海, 等. 辽宁中部城市灰霾天气数值模拟[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2014, 30 (6): 92- 99. |
| 11 |
李红斌, 傅瑜, 张靖萱, 等. 大连市冬季大气污染数值模拟及其对人工增雨(雪)作业的指示作用[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2017, 33 (5): 10- 16.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2017.05.002 |
| 12 | 刘香娥, 何晖, 贾星灿, 等. 北京一次污染天气过程特征的数值模拟[J]. 气象, 2016, 42 (9): 1096- 1104. |
| 13 |
马雁军, 王扬锋, 刘宁微. 辽宁中部城市群主要大气污染物时空分布特征的数值模拟[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2006, 22 (2): 6- 10.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2006.02.002 |
| 14 | 卢苗苗, 唐晓, 王自发, 等. 武汉地区2014年PM2.5时空分布与来源贡献的数值模拟研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37 (11): 4227- 4240. |
| 15 |
袁良, 王成林, 刘华强, 等. 长江三角洲地区低层大气污染物O3、NOx、SO2的数值模拟[J]. 环境监控与预警, 2011, 3 (1): 33- 37.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2011.01.010 |
| 16 | 高达, 谢旻, 陈星, 等. 气候变化对长三角臭氧污染影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 装备环境工程, 2019, 16 (6): 115- 122. |
| 17 | Schaap M , Timmermans R M A , Roemer M , et al. The LOTOS-EUROS model: description, validation and latest developments[J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2008, 32 (2): 270- 290. |
| 18 | Crippa M , Guizzardi D , Muntean M , et al. Gridded emissions of air pollutants for the period 1970-2012 within EDGAR v4.3.2[J]. Earth System Science Data Discussion, 2018, 10 (4): 1987- 2013. |
| 19 | Molteni F , Buizza R , Palmer T N , et al. The ECMWF ensemble prediction system: Methodology and validation[J]. Quarterly journal of the royal meteorological society, 1996, 122 (529): 73- 119. |
| 20 | Mizzi A P , Arellano A F , Edwards D P , et al. Assimilating compact phase space retrievals of atmospheric composition with WRF-Chem/DART: a regional chemical transport/ensemble Kalman filter data assimilation system[J]. Geoscientific Model Development(Discussions), 2015, 8 (9): 7693- 7725. |
| 21 | Boylan J W , Russell A G . PM and light extinction model performance metrics, goals, and criteria for three-dimensional air quality models[J]. Atmospheric environment, 2006, 40 (26): 4946- 4959. |
| 22 | 戴昭鑫, 张云芝, 胡云锋, 等. 基于地面监测数据的2013-2015年长三角地区PM2.5时空特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2016, 25 (5): 813- 821. |
| [1] | Ping JIANG,Xiao-ran LIU,Jun KANG,Dai-qiang LIAO,Jie ZHOU. Quantitative assessment of wind environment in neighborhoods based on exceeding probability in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 31-41. |
| [2] | LI Shuang, DING Zhi-ying, ZHAO Huan, XING Rui, KANG Xiao-yu, HAN Yan-feng. Analysis of multi-scale characteristics of a short-time rainstorm process in Liaoning province in 2014 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(6): 75-83. |
| [3] | WU Chang-guang, FANG Ya-ping, LIN Yao-yu, MA Xiao-yang, WANG Yao-wu, WANG Ke-huan. Analysis of the effect of street greenbelt on microclimate in a hot-humid area of China using a numerical simulation method [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(5): 99-106. |
| [4] | AI Kai, ZHENG Yi-qun, ZENG Xin-min, CHEN Hao-wei. Effect of different cloud microphysical parameterization schemes of WRF model on autumn precipitation over West China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(2): 1-10. |
| [5] | JIANG Yang, HE Zhi-xin, ZHOU Kun, ZHU Hong-fang, WANG Dong-yong. Analysis of forming reason of freezing rain weather and its characteristics in mountain and plain of Anhui province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(2): 11-17. |
| [6] | ZOU Xu-dong,YANG Hong-bin,ZHANG Yun-hai,LIU Yu-che,WANG Hong-yu. Numerical simulation of haze weather in the central cities of Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(6): 92-99. |
| [7] | ZHANG Nan,YI Xiao-yuan,ZHU Li-juan,WANG Qing-yuan. Analysis of two heavy snow/rain processes influenced by surface cyclone in North China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(5): 7-14. |
| [8] | WANG Kai-yan,DENG Tao, DENG Xue-jiao,LI Hai-yang,ZHAO Xiao-wei,QI Xiu-xiang. Numerical simulation analysis of a haze numerical forecast system in process of different synoptic types [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(5): 21-26. |
| [9] | WANG Jing,ZHAO Yu-jie,WU Zhen-ling,CAI Zi-ying . Effects of establishment of mixed layer on a strong gust weather process [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(4): 26-33. |
| [10] | CHENG Xiang-kun, CHENG Hang,XU Jie,MA Yan-jun. A numerical simulation test of a sea fog event over the Yellow Sea [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(6): 15-23. |
| [11] | XIE Jin-fan ,WANG Yu-kun ,ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Ting ,YU Li. The application of numerical simulation technique to macro-siting of wind farm [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(5): 148-153. |
| [12] | SONG Xiao-hui,TIAN Li-qing,TIAN Xiu-xia,MA Hong-qing,ZHANG Gong-wen,DONG Fang-liang. Numerical simulation on a return-flow snowstorm process in Hebei province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(3): 8-14. |
| [13] | WANG Wen,CHENG Pan. Numerical simulation and diagnostic analysis of a rainstorm process [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(1): 1-11. |
| [14] | ZOU Xu-dong,YANG Hong-bin,LI Shuai-bin,LIU Yu-che,WANG Hong-yu. Numerical simulation for a pollution weather process in Shengyang, Liaoning province using MM5 model and NCEP/NCAR data [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2012, 28(4): 8-15. |
| [15] | ZOU Xu-Dong, TIAN Xiao-Bo, YANG Hong-Bin, WANG Hong-Yu, LIU Yu-Che, ZHANG Yun-Hai. Simulation analysis of PM10 emission from typically atmospheric pollution sources in winter of 2007 over Shenyang [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2011, 27(6): 28-34. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
