国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 47-56.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2022.04.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tao WANG1,2( ),Yi-shu WANG1,Chun-yu ZHAO1,Xiao-tao WANG1,Mei-ou QIN1,Yu-min SHEN1,*(
),Yi-shu WANG1,Chun-yu ZHAO1,Xiao-tao WANG1,Mei-ou QIN1,Yu-min SHEN1,*( ),Yi-ling HOU1,Jian-yun ZHAO1
),Yi-ling HOU1,Jian-yun ZHAO1
Received:2021-04-25
Online:2022-08-28
Published:2022-09-22
Contact:
Yu-min SHEN
E-mail:nick_bsb@126.com
CLC Number:
Tao WANG, Yi-shu WANG, Chun-yu ZHAO, Xiao-tao WANG, Mei-ou QIN, Yu-min SHEN, Yi-ling HOU, Jian-yun ZHAO. Prediction model of first-frost date in Liaoning province using machine learning methods[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(4): 47-56.
Table 1
28 meteorological element fields from ERA5 reanalysis data"
| 序号 | 再分析数据28个气象要素场 |
| 1 | 500 hPa Geopotential(500 hPa位势高度) |
| 2 | 100 hPa Geopotential(100 hPa位势高度) |
| 3 | 500 hPaTemperature(500 hPa温度场) |
| 4 | 850 hPa U-component of wind(850 hPa纬向风场) |
| 5 | 850 hPa V-component of wind(850 hPa经向风场) |
| 6 | 700 hPa U-component of wind(700 hPa纬向风场) |
| 7 | 700 hPa V-component of wind(700 hPa经向风场) |
| 8 | 200 hPa U-component of wind(200 hPa纬向风场) |
| 9 | 200 hPa V-component of wind(200 hPa经向风场) |
| 10 | high_vegetation_cover(高植被覆盖比例) |
| 11 | leaf_area_index_high_vegetation(高植被用地所有叶子一侧表面积) |
| 12 | leaf_area_index_low_vegetation(低植被用地所有叶子一侧表面积) |
| 13 | low_vegetation_cover(低植被覆盖比例) |
| 14 | mean_sea_level_pressure(海平面气压) |
| 15 | snow_density(积雪密度) |
| 16 | snow_depth(积雪深度) |
| 17 | snowfall(累计降雪量) |
| 18 | soil_temperature_level_1(3.5 cm土壤温度) |
| 19 | soil_temperature_level_2(17.5 cm土壤温度) |
| 20 | soil_temperature_level_3(64.0 cm土壤温度) |
| 21 | soil_temperature_level_4(194.5 cm土壤温度) |
| 22 | soil_type(土壤类型) |
| 23 | type_of_high_vegetation(高植被类型) |
| 24 | type_of_low_vegetation(低植被类型) |
| 25 | volumetric_soil_water_layer_1(3.5 cm土壤含水量) |
| 26 | volumetric_soil_water_layer_2(17.5 cm土壤含水量) |
| 27 | volumetric_soil_water_layer_3(64.0 cm土壤含水量) |
| 28 | volumetric_soil_water_layer_4(194.5 cm土壤含水量) |
Fig.4
Spatial distribution of RMSE and the rate with the same sign of anomaly of the first-frost date in Liaoning province predicted by the Lasso Regression (a), Random Forest (b), and Neural Network (c) models with prediction starting from February (a1, b1, c1), March (a2, b2, c2), April (a3, b3, c3), May (a4, b4, c4), June (a5, b5, c5), and July (a6, b6, c6)"
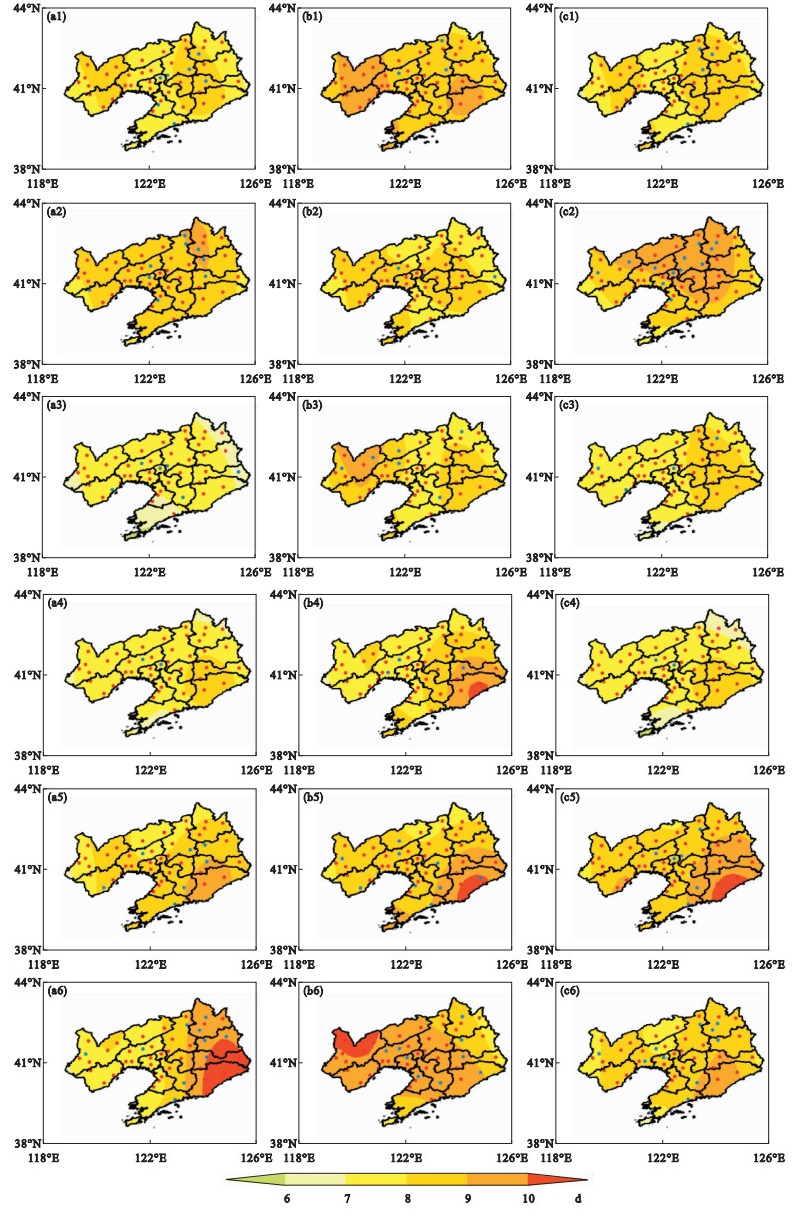
Table 2
Distribution of feature weights of the first-frost date in Liaoning province with prediction starting from February to July"
| 特征 | 起报时间 | ||||||
| 2月 | 3月 | 4月 | 5月 | 6月 | 7月 | 平均 | |
| 500 hPa位势高度 | -2.61 | -2.62 | -3.57 | -3.24 | -1.29 | -4.04 | -2.90 |
| 100 hPa位势高度 | 1.24 | 0.70 | -2.30 | 2.40 | 1.50 | -0.51 | 0.50 |
| 500 hPa温度场 | 2.12 | 1.07 | 5.00 | 1.03 | 1.84 | 4.25 | 2.55 |
| 850 hPa纬向风场 | 0.00 | -0.96 | -0.84 | -0.85 | -0.47 | -0.93 | -0.81 |
| 850 hPa经向风场 | -0.92 | -1.37 | -0.08 | 0.00 | 1.11 | 0.26 | -0.20 |
| 700 hPa纬向风场 | 0.53 | 1.17 | 1.36 | 1.08 | 2.28 | 1.09 | 1.25 |
| 850 hPa经向风场 | 1.27 | -0.26 | 0.30 | 0.00 | -0.33 | -1.53 | -0.11 |
| 200 hPa纬向风场 | 0.47 | -0.87 | -0.90 | 0.00 | -2.45 | 0.38 | -0.67 |
| 200 hPa经向风场 | -0.40 | 1.00 | -0.44 | 0.53 | -0.40 | 0.00 | 0.06 |
| 高植被覆盖比例 | -2.88 | -2.86 | -2.53 | -2.48 | -2.89 | -5.06 | -3.12 |
| 高植被用地所有叶子一侧表面积 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.56 | 0.27 |
| 低植被用地所有叶子一侧表面积 | -3.27 | -2.56 | -2.02 | -2.75 | -1.16 | 0.21 | -1.93 |
| 低植被覆盖比例 | -7.10 | -7.11 | -6.01 | -6.14 | -5.03 | -6.55 | -6.33 |
| 海平面气压 | 1.03 | 0.72 | 1.14 | 1.01 | -0.37 | 1.42 | 0.83 |
| 积雪密度 | -1.16 | -2.93 | -1.82 | -0.96 | -0.24 | -0.58 | -1.28 |
| 积雪深度 | -2.08 | -0.28 | -0.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -0.71 |
| 累计降雪量 | 0.63 | 0.41 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.30 |
| 3.5 cm土壤温度 | -5.14 | -2.84 | 0.19 | 2.24 | -1.89 | 8.85 | 0.24 |
| 17.5 cm土壤温度 | 9.02 | 4.58 | 1.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -14.82 | -0.04 |
| 64.0 cm土壤温度 | -1.92 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 4.96 | 12.35 | 3.17 |
| 194.5 cm土壤温度 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 3.16 | 2.23 | 0.26 | -1.68 | 0.88 |
| 土壤类型 | 1.87 | 1.47 | 1.40 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.84 | 1.45 |
| 高植被类型 | 0.00 | -0.49 | -0.45 | 0.00 | -0.32 | -0.77 | -0.51 |
| 低植被类型 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -0.01 | 0.00 | -0.20 | -0.20 | -0.14 |
| 3.5 cm土壤含水量 | 0.87 | 1.28 | -0.39 | -6.57 | -4.14 | -3.95 | -2.15 |
| 17.5 cm土壤含水量 | -2.56 | -1.00 | -0.37 | 7.55 | 1.86 | 0.00 | 1.10 |
| 64.0 cm土壤含水量 | 4.95 | 4.15 | 5.55 | 3.17 | 5.56 | 5.31 | 4.78 |
| 194.5 cm土壤含水量 | -0.52 | -1.79 | -2.42 | -1.90 | -1.34 | 0.00 | -1.59 |
| 1 | 李彩霞, 李俏, 孙天一, 等. 气候变化对黑龙江省主要农作物产量的影响[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2014, 23 (6): 200- 208. |
| 2 | 钱锦霞, 武捷, 班胜林. 1951—2008年太原市霜冻发生特征分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25 (10): 287- 289. |
| 3 | 申双和, 仲宇翔, 李鹏飞. 近54a三江平原地区初霜冻指标特征研究[J]. 气象科学, 2018, 38 (3): 378- 384. |
| 4 |
郑红, 魏磊, 潘华盛, 等. 黑龙江终霜日变化特征及对粮食生产影响的分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32 (11): 88- 94.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15090093 |
| 5 | 张磊, 王静, 张晓煜. 近50a宁夏初、终霜日基本特征及变化趋势[J]. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31 (6): 1039- 1045. |
| 6 |
敖雪, 翟晴飞, 崔妍, 等. 不同升温情景下中国东北地区平均气候和极端气候事件变化预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (5): 40- 51.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2020.05.006 |
| 7 | 王国复, 许艳, 朱燕君, 等. 近50年我国霜期的时空分布及变化趋势分析[J]. 气象, 2009, 35 (7): 61- 67. |
| 8 | 李想, 陈丽娟, 张培群. 1954—2005年长江以北地区初霜期变化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4 (1): 21- 25. |
| 9 | 韩荣青, 李维京, 艾婉秀, 等. 中国北方初霜冻日期变化及其对农业的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 65 (5): 525- 532. |
| 10 | 孙惠合, 晁林海. 基于多模型离散覆盖的宿州初霜期动态灰预测[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24 (11): 379- 383. |
| 11 | 陆忠艳, 韩江文, 李萍, 等. 辽宁省初霜特征及预报技术指标初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30 (36): 257- 263. |
| 12 | 曲成军, 林嘉楠, 赵广娜. 近50年黑龙江省初霜日变化影响因子及预测模型建立的研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2019, 28 (3): 205- 213. |
| 13 | Tong X , Yan Z W , Xia J J , et al. Decisive atmospheric circulation indices for July-August precipitation in North China based on tree models[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2019, 20 (8): 1707- 1720. |
| 14 | Gao L H , Wei F Y , Yan Z W , et al. A study of objective prediction for summer precipitation patterns over eastern China based on a multinomial logistic regression model[J]. Atmosphere, 2019, 10 (4): 213. |
| 15 | 孙苏琪, 王式功, 罗彬, 等. 应用机器学习算法的成都市冬季空气污染预报研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (2): 98- 104. |
| 16 | Moon S H , Kim Y H . An improved forecast of precipitation type using correlation-based feature selection and multinomial logistic regression[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2020, 240, 104928. |
| 17 | 孙全德, 焦瑞莉, 夏江江, 等. 基于机器学习的数值天气预报风速订正研究[J]. 气象, 2019, 45 (3): 426- 436. |
| 18 | Kim S J , Koh K , Lustig M , et al. An interior-point method for large-scale l1-regularized least squares[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1 (4): 606- 617. |
| 19 | Friedman J , Hastie T , Tibshirani R . Regularization path for generalized linear models by coordinate descent[J]. Journal of Statistical Software, 2010, 33 (1): 1- 22. |
| 20 | Breiman L . Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45, 5- 32. |
| 21 | Geurts P , Ernst D , Wehenkel L . Extremely randomized trees[J]. Machine Learning, 2006, 63, 3- 42. |
| 22 | Glorot X, Bengio Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks[C]//PMLR. Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Chia Laguna Resort, Sardinia, Italy: PMLR, 2010, 9: 249-256. |
| 23 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]//IEEE. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015: 1026-1034. |
| 24 | 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 248- 261. |
| [1] | Nan FANG, Guo-quan XIE, Xiao-jian RUAN, Chen-ping REN, Shu-jie JIANG, Wei-wei ZHANG. Application of long short-term memory neural network (LSTM) model in low visibility forecast [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(5): 34-41. |
| [2] | Sheng-dong LU, Jun-xia LI, Fen LI, Jun-jie ZHAO, Ze-hui JIN, Ying LI, Xiao LIU. Analysis of the characteristics of O3 concentration and its influencing factors in summer from 2017 to 2019 in the southern urban area of Taiyuan [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(3): 40-46. |
| [3] | Yan-lan LI,Long JIN,Xu-ming SHI,Dan CHEN. Study on assessment model of typhoon disaster in Guangxi based on genetic-neural network method [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(3): 139-144. |
| [4] | Yuan-mou WANG,Jia-qi LI,Shi-ji CHEN,Jia-ping TANG,Bai-cheng XIA,Shi-gang HAN. Identification of the fog image features on the Yangtze River waterways in Chongqing based on machine learning [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(1): 106-112. |
| [5] | Yu HAN,Guo-bing ZHOU,Dao-jin CHEN,Chun YANG,Fan-hua MIN. Characteristics of ozone pollution and forecasting technique based on meteorological factors in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(4): 59-66. |
| [6] | Xu FAN,Ying HUANG,Wen-nan LENG,Bei-dou ZHANG,Wen-yu ZHANG,Guo-yin WANG. Inversion of ground-based microwave radiometer measurements using radial basis function neural network [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(2): 62-69. |
| [7] | DU Qin-bo, WU Xiao-yan, ZHENG Su-fan, LI Yue-ying, CHEN Huan-huan, ZHANG Yu-feng. Effects of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 pollution in Shantou and the PM2.5 prediction [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(5): 70-77. |
| [8] | QU Jian-hua, YAN Jun-jie, XUE Juan, GUO Xue-xing. Research on the cloud detection model of FY3D/MERSI and EOS/MODIS based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(3): 87-93. |
| [9] | LIU Bo; DANG Bing; ZHANG Nan;WANG Shi-gong; YIN Ling; ZHANG Xiao-yun; LI Tan-shi;LU Zhen-hua. Comparison of various meteorological statistical forecasting models-Taking causing- stroke weather forecasting as an example [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(4): 126-133. |
| [10] | LI Xiao-lan, LIU Yang, LUAN Jian, MA Yan-jun, WANG Yang-feng, ZHANG Wan-ying. Integration forecast experimentation for PM2.5 mass concentration in Shenyang based on BP artificial neural network [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(2): 100-106. |
| [11] | WANG Huan-yi, TAN Zheng-hua, YANG Meng, ZHANG Qiao, JIANG Lin-shan. Research on air temperature product examination of three numerical forecast and a method of error correction [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(1): 22-29. |
| [12] | HUANG Hai-jing, ZHANG Jing-hong, QIN Wen-na, ZHANG Ming-jie, XING Cai-ying. Forecast of hourly total solar radiation based on a wavelet back propagation neural network method in Hainan province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(1): 60-65. |
| [13] | JIANG Ying,SHEN Yan-bo,DANG Jun. Comparison on two prediction methods of minutely global solar radiation [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(3): 85-91. |
| [14] | YANG Yong-sheng HE Ping . Comparison on early flood season precipitation prediction between projection pursuit regression method and back propagation neural network method [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2008, 24(1): 14-17. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|