国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 25-33.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2022.05.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jing LIU1,2( ),Chuan-lei CHEN2,Ying WANG2,Kui-zhi CAI2,*(
),Chuan-lei CHEN2,Ying WANG2,Kui-zhi CAI2,*( ),Chuan REN3,Wei DONG4
),Chuan REN3,Wei DONG4
Received:2021-01-05
Online:2022-10-28
Published:2022-11-04
Contact:
Kui-zhi CAI
E-mail:liujing-syau@163.com;ckz_ivan@163.com
CLC Number:
Jing LIU, Chuan-lei CHEN, Ying WANG, Kui-zhi CAI, Chuan REN, Wei DONG. Comparison of neighborhood verification of radar echo forecast in Liaoning province using four high-resolution models[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(5): 25-33.
Table 2
Occurrence date of selected convective weather processes in Liaoning province in 2017 and 2018"
| 序号 | 区域性降水时间 | 局地性降水时间 |
| 1 | 2017-07-22 | 2017-06-19 |
| 2 | 2017-08-27 | 2017-07-09 |
| 3 | 2017-08-15 | 2017-07-13 |
| 4 | 2017-08-24 | 2017-07-14 |
| 5 | 2017-09-07 | 2017-09-10 |
| 6 | 2018-07-08 | 2018-06-17 |
| 7 | 2018-08-14 | 2018-07-09 |
| 8 | 2018-08-18 | 2018-08-13 |
| 9 | 2018-08-23 | 2018-08-20 |
| 10 | 2018-09-15 | 2018-09-02 |
Table 3
Setting parameters of the four high-resolution models"
| 模式名称 | 区域 | 空间分辨率 | 时间分辨率 | 范围 | 调整后范围 |
| 华东模式 | 华东区域 | 0.03°×0.03° | 逐小时 | 5°~60°N 50°~160°E | 37°~46°N 115°~127°E |
| 华北模式 | 华北区域 | 0.03°×0.03° | 逐小时 | 33°~48°N 104°~124°E | 37°~46°N 115°~127°E |
| GRAPES_3km | 全国重点区域 | 0.03°×0.03° | 逐小时 | 10°~60°N 70°~145°E | 37°~46°N 115°~127°E |
| 睿图东北 | 东北地区 | 0.03°×0.03° | 逐小时 | 37°~54°N 112°~135°E | 37°~46°N 115°~127°E |
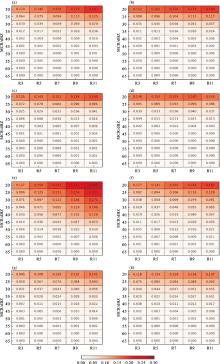
Fig.1
Radar echo forecasts for regional precipitation processes in Northeast China from June to September in 2017 and 2018 using the East China Model (a), the North China Model (b), the GRAPES Model (c), and the Northeast China WRF Model (d), and the results for local precipitation processes (e-h)"
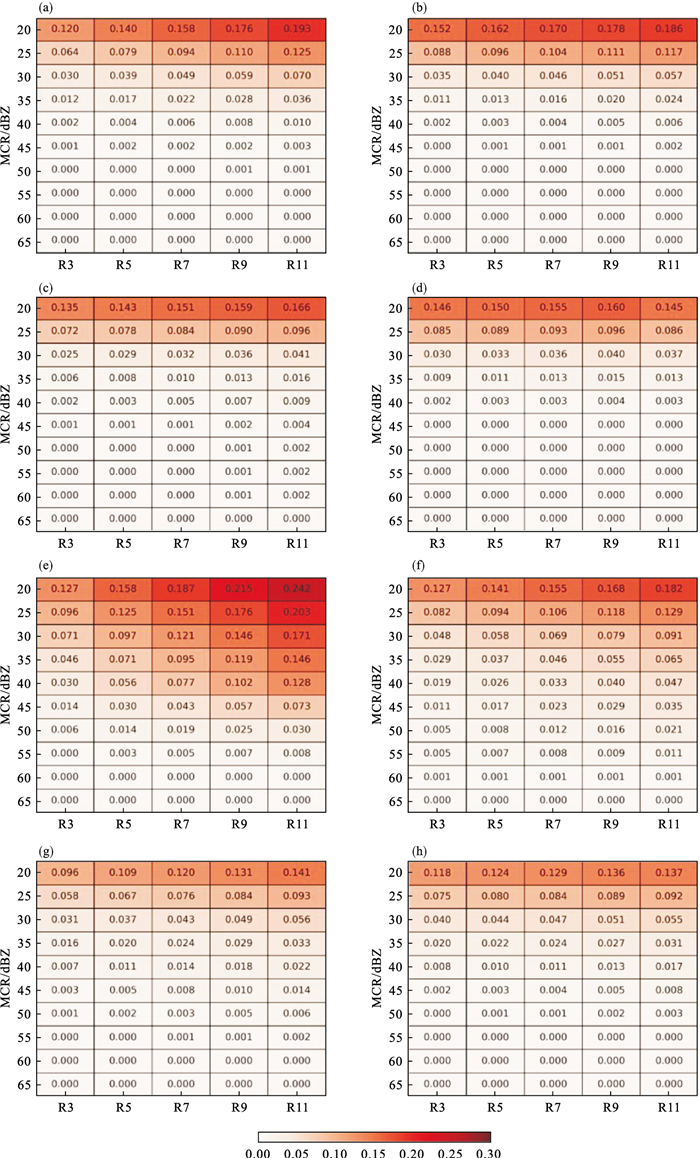
Fig.3
Comparison of forecast skills of radar echo using four high-resolution models with the neighborhood radius of 3 km (a1), 5 km (b1), 7 km (c1), 9 km (d1), and 11 km for regional precipitation and local precipitation (a2, b2, c2, d2) in Northeast China from June to September in 2017 and 2018"
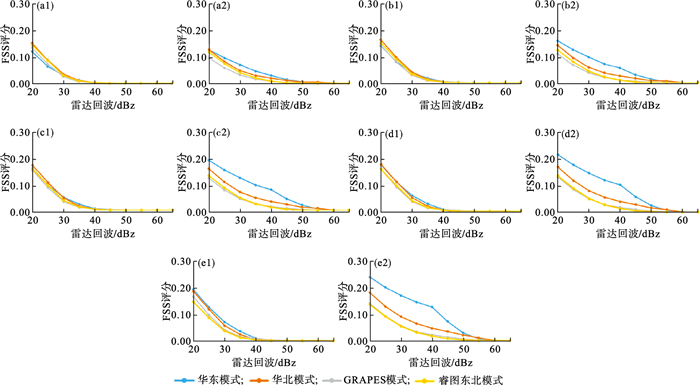
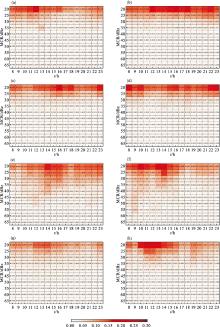
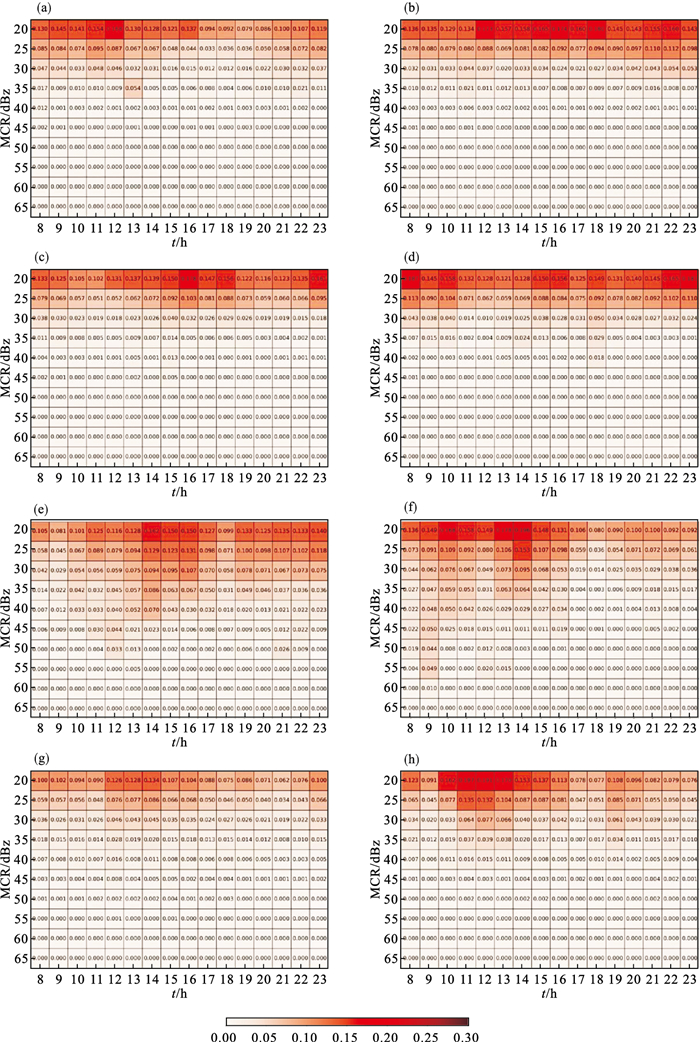
Fig.4
Variation of FSS of radar echo forecasts for regional precipitation processes in Northeast China from June to September in 2017 and 2018 using the East China Model (a), the North China Model (b), the GRAPES Model (c), and the Northeast China WRF Model (d), and the results for local precipitation processes (e-h)"
| 1 | 辽宁省地方志编撰委员会办公室. 辽宁省志·气象志[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁民族出版社, 2015: 9. |
| 2 | 杨吉, 郑媛媛, 夏文梅, 等. 雷达拼图资料上中尺度对流系统的跟踪与预报[J]. 气象, 2018, 41 (6): 738- 744. |
| 3 | 卢冰, 孙继松, 仲跻芹, 等. 区域数值预报系统在北京地区的降水日变化预报偏差特征及成因分析[J]. 气象学报, 2017, 75 (2): 248- 259. |
| 4 | 雷蕾, 孙继松, 王国荣, 等. 基于中尺度数值模式快速循环系统的强对流天气分类概率预报试验[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70 (4): 752- 765. |
| 5 |
唐娴, 周荣卫, 向晓风, 等. 多源降水预报集成技术应用研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37 (4): 26- 32.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2021.04.004 |
| 6 |
闫之辉, 邓莲堂. WRF模式中的微物理过程及其预报对比试验[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2007, 1 (6): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0799.2007.06.001 |
| 7 |
卢萍, 宇如聪, 周天军. 2003年8月"巴蜀夜雨"过程的模拟和分析研究[J]. 气象学报, 2008, 66 (3): 371- 380.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2008.03.008 |
| 8 | 张涵斌, 范水勇, 陈敏, 等. 区域集合预报基于SKEB和多物理过程的混合模式扰动方法研究[J]. 气象, 2019, 45 (1): 17- 28. |
| 9 |
Berner J , Ha S Y , Hacker J P , et al. Model uncertainty in a mesoscale ensemble prediction system: Stochastic versus Multiphysics representations[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2011, 139 (6): 1972- 1995.
doi: 10.1175/2010MWR3595.1 |
| 10 |
Bowler N E , Arribas A , Mylne K R , et al. The MOGREPS short-range ensemble prediction system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2008, 134, 703- 722.
doi: 10.1002/qj.234 |
| 11 |
袁月, 李晓莉, 陈静, 等. GRAPES区域集合预报系统模式不确定性的随机扰动技术研究[J]. 气象, 2016, 42 (10): 1161- 1175.
doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.10.001 |
| 12 |
付宗钰, 于波, 荆浩, 等. 联合概率方法在北京灾害天气预报中的应用研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (5): 1- 9.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2020.05.001 |
| 13 |
Germer M , Fischer T , Jiang T , et al. Trends in precipitation extremes in the Zhujiang River Basin, South China[J]. Climate, 2011, 24 (3): 750- 761.
doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3717.1 |
| 14 | 李超, 裘薇, 娄小芬, 等. 浙江省温度和相对湿度释用技术及其效果检验分析[J]. 气象科学, 2016, 36 (4): 556- 561. |
| 15 | 杨关盈, 邓学良, 王磊, 等. 基于CUACE模式产品的订正方法比较研究[J]. 气象科学, 2018, 37 (6): 839- 844. |
| 16 | 范江琳, 曹萍萍, 肖递祥, 等. 西南区域中心模式SWC-WARMS降水偏差分析[J]. 气象科学, 2019, 39 (3): 349- 358. |
| 17 | 梅钦, 智协飞, 王佳. WRF模式不同云参数化方案的暴雨预报能力检验及集成试验[J]. 大气科学学报, 2018, 41 (6): 731- 742. |
| 18 |
刘静, 才奎志, 谭政华. 高分辨率模式雷达回波预报能力分析[J]. 气象, 2019, 45 (12): 1710- 1717.
doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2019.12.008 |
| 19 | Baldwin M E , Kain J S . Sensitivity of several performance measures to displacement error, bias, and event frequency[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2006, 21 (4): 636- 684. |
| 20 | Schwartz C S , Kain J S , Weiss S J , et al. Toward improved convection-allowing ensembles: Model physics sensitivities and optimizing probabilistic guidance with small ensemble membership[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2010, 25 (1): 263- 280. |
| 21 | Mittermaier M , Roberts N . Intercomparison of spatial forecast verification methods: Identifying skillful spatial scales using the fractions skill score[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2010, 25 (1): 343- 354. |
| 22 | 唐文苑, 郑永光, 张小雯. 基于FSS的高分辨率模式华北对流预报能力评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 2018, 29 (5): 513- 523. |
| 23 | 马申佳, 陈超辉, 智协飞, 等. 基于时空不确定性的对流尺度集合预报效果评估检验[J]. 气象学报, 2018, 76 (4): 578- 589. |
| 24 | 金巍, 刘卫华, 高凌峰, 等. 辽宁地区ECMWF模式气温预报检验及误差订正研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (6): 50- 57. |
| [1] | Qi-ru DONG, Xiao-bin QIU, Ying WANG, Ze-lin WANG, Ji LI, Mian LIANG. Improvement of nowcasting for a squall line using cycling assimilation radar data [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(3): 1-11. |
| [2] | Ping JIANG,Xiao-ran LIU,Jun KANG,Dai-qiang LIAO,Jie ZHOU. Quantitative assessment of wind environment in neighborhoods based on exceeding probability in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 31-41. |
| [3] | An-qi NIE,De-qin LI,Fang-da TENG,Jing-long LU,Dang WANG. Verification of multi-model precipitation forecast in Liaoning province in summer and research on clear or rain forecast method [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(5): 10-17. |
| [4] | Tao WANG, Yi-shu WANG, Yu-min SHEN, Yan WANG, Lian-wei ZHAO, Xiao-tao WANG, Li-du SHEN. Assessment of air temperature simulation and threshold-crossing times of 2 ℃ warmings by CMIP5 models in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(2): 49-61. |
| [5] | BAN Jin, WANG Bo, LI Yong-sheng, ZHAO Jia-ying. Prediction of summer precipitation in Heilongjiang province based on the NCEP_CFSv2 model [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(6): 21-27. |
| [6] | MENG Ying-ying, CAO Dian-bin, WU Yan, WANG Zi-yang. Comparisons of dynamic downscaling of the wind field in forest areas of Da-Xiao-Xing'anling Mountains [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(4): 8-15. |
| [7] | GAO Shu-xin, SONG Xiao-wei, LI Lin-lin, XUE Yi, CHEN Peng-xin, QI Wen-chuan. Applicability evaluation of the GLIGEN weather generator on the simulation of temperature in three provinces of Northeast China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(4): 77-84. |
| [8] | WANG Ye-hong, ZHAO Yu-chun. Impacts of different background error samples simulation schemes on numerical forecast-taking typhoon “Soudelor” as an example [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(6): 11-23. |
| [9] | SHEN Li-du, GONG Qiang, XU Hong, WANG Tao, GU Zheng-qiang, MA Yan-jun. A numerical simulation study on the effects of urban expansion on the wind and thermal environment in boundary layer:a case study of Shenyang [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(6): 64-74. |
| [10] | JI Yong-ming1 JIANG Da-kai2 CHEN Chuan-lei;REN Zhi-jie;MENG Ying;CAI Kui-zhi; HU Peng-yu;ZHANG Shuo. Quantitative precipitation inversion algorithm based on the multi-radar mosaic I: dynamic Z-I relationships [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(4): 18-25. |
| [11] | XU Shu;WEI Ying-hua;XIONG Ming-ming;WEI Lin. Application of Frequency-Matching method to ECMWF ensemble statistic fusing prediction products in the Haihe River basin [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(4): 11-17. |
| [12] | WANG Huan-yi, TAN Zheng-hua, YANG Meng, ZHANG Qiao, JIANG Lin-shan. Research on air temperature product examination of three numerical forecast and a method of error correction [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(1): 22-29. |
| [13] | YANG Lei, WANG Ying, SUN Li, LIU Rui-xia, CAI Kui-zhi, LI Ming-jian. Introduction of LAPS and its application in a rainstorm case in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(6): 1-8. |
| [14] | LIU Hui, RAO Xiao-qin, ZHANG Heng-de, LI Ming, ZHANG Zhi-gang. Comparative verification and analysis of environmental meteorology operational numerical prediction models in China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(5): 17-24. |
| [15] | YANG Yang, WANG Lian-zhong, ZHOU Xiao-shan. Establishment and application of the verification and evaluation system of operational model forecast products in Northeast China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(4): 21-28. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|