国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 9-16.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2024.03.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lei YAO1,2( ),Jiaren YAN1,2,*(
),Jiaren YAN1,2,*( ),Ruixiang LIU1,2
),Ruixiang LIU1,2
Received:2023-07-22
Online:2024-06-28
Published:2024-08-09
Contact:
Jiaren YAN
E-mail:502115889@qq.com;yan_jiaren@126.com
CLC Number:
Lei YAO, Jiaren YAN, Ruixiang LIU. A polluted weather analysis in Lianyungang area based on unmanned aerial vehicle vertical observation[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 9-16.
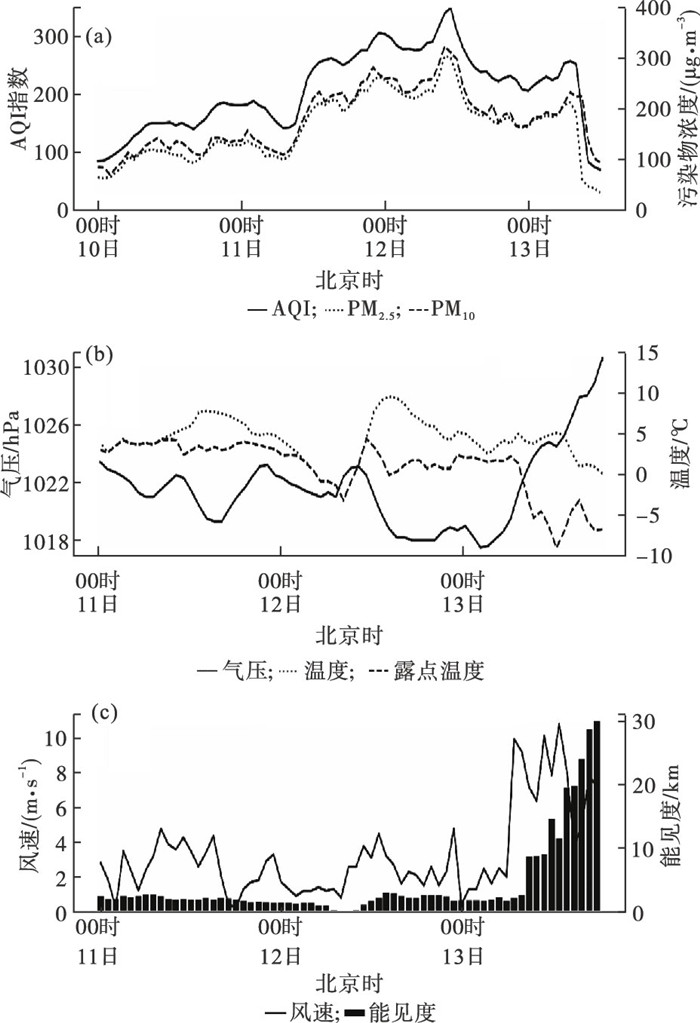
Fig.1
Variation of hourly mean surface concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10, air quality index (AQI) from December 11 to 13 (a), and variation of hourly mean air pressure, air temperature, and dew-point temperature (b), as well as wind speed and atmospheric visibility (c) from December 11 to 13, 2020, in Lianyungang area"
| 1 | 吴兑. 灰霾天气的形成与演化[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34 (3): 157- 161. |
| 2 | 宋娟, 程婷, 谢志清, 等. 江苏省快速城市化进程对雾霾日时空变化的影响[J]. 气象科学, 2012, 32 (3): 275- 281. |
| 3 | 孙志豪, 崔燕平. PM2.5对人体健康影响研究概述[J]. 环境科技, 2013, 26 (4): 75- 78. |
| 4 | 李洪枚, 伍鹏程, 伯鑫, 等. 临沂市区主要大气污染物的污染特征及其对居民健康的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40 (8): 2919- 2934. |
| 5 | 赵慧霞, 王维国, 李泽椿, 等. 雾对我国交通运输的不利影响及对策[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2010, 26 (2): 58- 62. |
| 6 |
Xue T , Liu J , Zhang Q , et al. Rapid improvement of PM2.5 pollution and associated health benefits in China during 2013-2017[J]. Science China Earth Science, 2019, 62 (12): 1847- 1856.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9348-2 |
| 7 |
Zhai S X , Jacob D J , Wang X , et al. Fine particulate matter(PM2.5) trends in China, 2013-2018:separating contributions from anthropogenic emissions and meteorology[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 19 (16): 11031- 11041.
doi: 10.5194/acp-19-11031-2019 |
| 8 | 陈璇, 王晓玲, 陈赛男, 等. 不同天气型下武汉城市圈PM2.5污染及大气层结特征分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42 (8): 52- 63. |
| 9 | 郝春旭, 邵超峰, 董战峰, 等. 2020年全球环境绩效指数报告分析[J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48 (16): 68- 72. |
| 10 | 曾琳, 伍志方, 范绍佳, 等. 基于风廓线雷达的广州边界层局地回流指数廓线对污染物浓度的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42 (6): 274- 284. |
| 11 | 陈媛, 岑况, NorraS, 等. 北京市区大气气溶胶PM2.5污染特征及颗粒物溯源与追踪分析[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24 (2): 345- 354. |
| 12 | 杨洋, 王红磊, 侯雪伟, 等. 石家庄一次持续性霾过程形成原因及气溶胶垂直探空分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37 (3): 824- 832. |
| 13 | 张静, 刘端阳, 钱映月, 等. 一次持续性雾霾天气的边界层结构特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36 (3): 483- 491. |
| 14 | 宋明昊, 张小玲, 袁亮, 等. 成都冬季一次持续污染过程气象成因及气溶胶垂直结构和演变特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40 (2): 408- 417. |
| 15 | 张思齐, 郭艳君, 王国复. 中国探空观测与第3代再分析大气湿度资料的对比研究[J]. 气象学报, 2018, 76 (2): 289- 303. |
| 16 | 王宏斌, 吴泓, 李永, 等. 旋翼无人机盐城试验观测资料分析及其在一次浓雾天气观测中的应用[J]. 气象, 2020, 46 (1): 89- 97. |
| 17 | 黄思源, 王界, 全彩峰. 2015年宁波地区两次灰霾天气过程气溶胶垂直分布特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2017, 33 (3): 45- 51. |
| 18 | 徐家平, 赵天良, 陈燕, 等. 基于旋翼无人机的大气边界层环境气象垂直观测及订正方法的研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2022, 38 (3): 101- 111. |
| 19 | 姜明, 史静, 姚巍, 等. 多旋翼微型无人机气象探测适用性分析[J]. 气象科技, 2018, 46 (3): 479- 484. |
| 20 | 鲁斯嘉, 王东生, 李小兵, 等. 基于无人机平台的细颗粒物三维分布监测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17 (8): 94- 100. |
| 21 | 李杨, 马舒庆, 贾小芳, 等. 基于无人直升机探测的北京地区重雾霾天气大气颗粒物垂直变化特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2016, 32 (6): 179- 183. |
| 22 | 曹云擎, 王体健, 高丽波, 等. 基于无人机垂直观测的南京PM2.5污染个例研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2020, 25 (3): 292- 304. |
| 23 | 陈树成, 李晓波, 崔明, 等. 不同天气条件下微波辐射计和风廓线雷达探测数据误差特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37 (1): 67- 72. |
| [1] | Wen-li LÜ,Xiao-meng SHI,Kai ZHANG. Visibility characteristics and influencing factors of a fog-haze process in Qingdao [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(3): 47-55. |
| [2] | Wei GUO, Ling-yun ZHU, Wen-ya WANG, Xing-ai GAO, Peng-wei CHENG, Yue-jun ZHANG. Evaluation of air quality improvement in Taiyuan during Second National Youth Games [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(6): 36-43. |
| [3] | Jun SHI, Yu-jie ZHAO. Analysis of the characteristics and influencing factors of a persistent fog and haze weather process in Dongli District, Tianjin [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(5): 8-12. |
| [4] | Yu ZHOU,Hong-xing HAN,Chen-xiao SHI,Jun XING,Li SUN. Comparative analysis of aerosol mass concentration characteristics in winter and spring during 2016 to 2017 in three cities of Hainan province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 82-90. |
| [5] | Feng-xiang LONG, Yu-lin ZHANG. Relationship between atmospheric visibility and particulate matter concentration and meteorological parameters in Guilin urban area [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(1): 21-27. |
| [6] | KANG Zeng-mei, LI Zhong-liang, LIU Wei, DONG Xiao-bo, MAI Rong, SUN Yu-wen. Aircraft observations on physical properties of precipitation clouds in Hebei province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(4): 1-7. |
| [7] | WU Wen-yu, ZHANG Hao, HE Bin-fang, HUO Yan-feng, ZHANG Hong-qun, ZHAI Jing. Spatiotemporal characteristics of criteria air pollutants during the critical period of straw burning in Huaihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(4): 33-39. |
| [8] | HU Cai-jiao, LI Jin-lun, WANG Zu-wu, CHENG Hai-rong, KE Hao-hao, WU Wan-ye. Characteristics of atmospheric PM10 and PM2.5 mass concentrations in Huangshi city [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(4): 40-46. |
| [9] | WU Jun-wei, ZHAO Hu-jia, YANG Dong, WEI Yao. Ground-based observation of aerosol optical properties in Pengzhou,Chengdu [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(2): 32-39. |
| [10] | JIANG Jiang, GUO Wen-li, WANG Chun-ling. Temporal and spatial characteristics of visibility in Beijing from 2007 to 2015 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(1): 45-52. |
| [11] | LI Xiao-lan, LIU Yang, LUAN Jian, MA Yan-jun, WANG Yang-feng, ZHANG Wan-ying. Integration forecast experimentation for PM2.5 mass concentration in Shenyang based on BP artificial neural network [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(2): 100-106. |
| [12] | LI Yang, ZHAO Hu-jia, MA Yan-jun, ZHU Yi-ming, LI Xiao-xiao. Variation characteristics of particulate matter and its correlations with meteorological elements over Benxi [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(1): 58-65. |
| [13] | LI Yang, MA Shu-qing, JIA Xiao-fang, ZHENG Yu, LU Sai, ZHAO Hu-jia. Vertical distribution of atmospheric particulate matter during a heavy fog-haze event in Beijing observed by an unmanned aerial vehicle [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(6): 179-183. |
| [14] | CHEN Bo-li, LEI Zheng-cui, WU Jian-qiu, WU Jing-lu, HUANG Wen-yan. Analysis on a persistent haze process in Changzhou [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(3): 34-40. |
| [15] | WANG Cheng-xiang, LIU Jia-zhen. Analysis of air quality situation and pollution reasons in Liaocheng [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(1): 108-112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|