国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 33-42.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2021.01.005
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xue AO1( ),Chun-yu ZHAO1,*(
),Chun-yu ZHAO1,*( ),Yan CUI1,Xiao-yu ZHOU1,Qing-fei ZHAI2,Li-du SHEN1,Tao WANG1
),Yan CUI1,Xiao-yu ZHOU1,Qing-fei ZHAI2,Li-du SHEN1,Tao WANG1
Received:2020-06-02
Online:2021-02-28
Published:2021-01-21
Contact:
Chun-yu ZHAO
E-mail:aoxuefyh@163.com;springrainscn@163.com
CLC Number:
Xue AO,Chun-yu ZHAO,Yan CUI,Xiao-yu ZHOU,Qing-fei ZHAI,Li-du SHEN,Tao WANG. Evaluation and projection of temperature change in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(1): 33-42.
Table 1
Differences in average temperature between the results simulated by RegCM4 and CMIP5 and observations from 1986 to 2005 in Northeast China ℃"
| 模式和观测 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 |
| RegCM4 | 5.08(-0.69) | 5.96(-1.05) | 20.97(-0.6) | 5.82(-0.74) | -11.76(0.61) |
| CMIP5 | 4.35(-1.42) | 5.03(-1.98) | 20.49(-1.08) | 5.16(-1.4) | -13.24(-0.87) |
| OBS | 5.77 | 7.01 | 21.57 | 6.56 | -12.37 |
Table 2
Results of relative changes of the annual and seasonal surface temperature in Northeast China from 2020-2035, 2046-2065, and 2080-2098 predicted by the RegCM4 and CMIP5 models (relative to those from 1986 to 2005) ℃"
| 模式 | 2020—2035年 | 2046—2065年 | 2080—2098年 | ||||||||||||||
| 年 | 春 | 夏 | 秋 | 冬 | 年 | 春 | 夏 | 秋 | 冬 | 年 | 春 | 夏 | 秋 | 冬 | |||
| RegCM4 RCP2.6 | 1.3 | 1.31 | 1.1 | 1.32 | 1.48 | 1.37 | 1.36 | 1.19 | 1.44 | 1.56 | 1.51 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 1.6 | 1.67 | ||
| RegCM4 RCP4.5 | 1.34 | 1.42 | 1.13 | 1.34 | 1.50 | 2.65 | 2.31 | 2.49 | 2.82 | 2.84 | 3.46 | 2.85 | 3.05 | 3.86 | 3.95 | ||
| RegCM4 RCP8.5 | 1.43 | 1.45 | 1.24 | 1.47 | 1.56 | 3.32 | 3.1 | 3.06 | 3.53 | 3.62 | 5.5 | 4.91 | 5.12 | 5.76 | 6.31 | ||
| CMIP5 RCP2.6 | 1.11 | 0.89 | 1.06 | 1.21 | 1.27 | 1.47 | 1.15 | 1.51 | 1.65 | 1.55 | 1.58 | 1.29 | 1.47 | 1.71 | 1.57 | ||
| CMIP5 RCP4.5 | 1.13 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 1.22 | 1.29 | 2.05 | 1.75 | 2.01 | 2.23 | 2.21 | 2.54 | 2.08 | 2.44 | 2.76 | 2.84 | ||
| CMIP5 RCP8.5 | 1.27 | 1.02 | 1.16 | 1.38 | 1.47 | 2.93 | 2.49 | 2.87 | 3.17 | 3.23 | 5.39 | 4.63 | 5.05 | 5.61 | 6.28 | ||
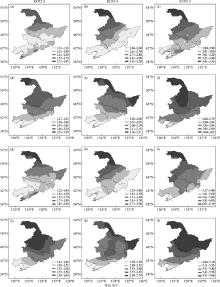
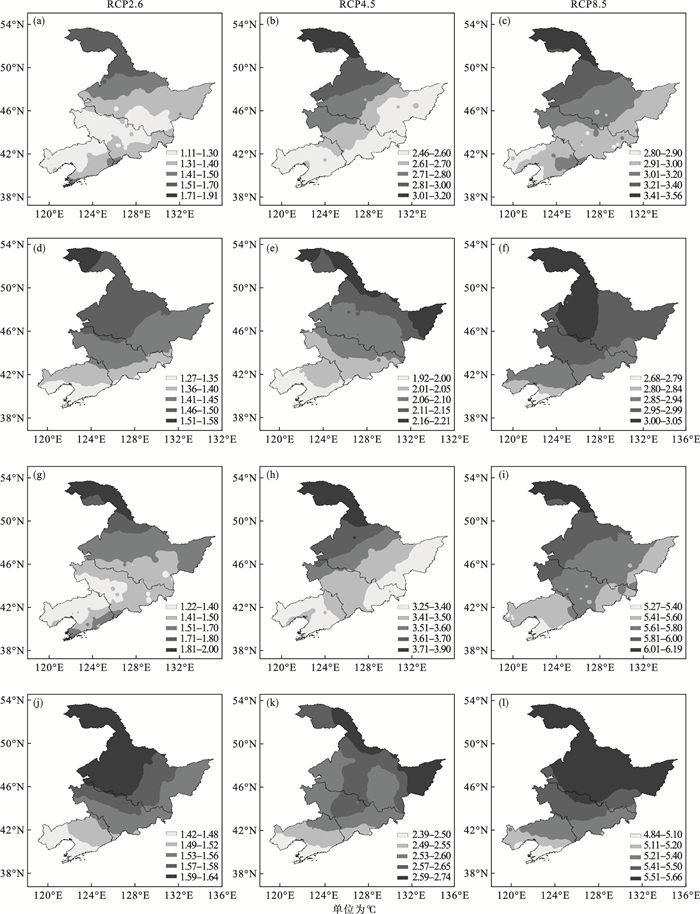
Fig.5
Spatial distributions of change in annual mean surface temperature in Northeast China from 2046-2065 (a, b, c, d, e, f) and 2081-2100 (g, h, i, j, k, l) under the RCP2.6 (a, d, g, j), RCP4.5 (b, e, h, k), RCP8.5 (c, f, i, l) predicted by the RegCM4 (a-c, g-i) and CMIP5 (d, e, f, j, k, l) models (relative to those from 1986 to 2005)"
| 1 | 秦大河, StockerT, 等. IPCC第五次评估报告第一工作组报告的亮点结论[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10 (1): 1- 6. |
| 2 | IPCC . Climate change 2013: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013. |
| 3 |
Gao X J , Zhao Z C , Ding Y H , et al. Climate change due to greenhouse effects in China as simulated by a regional climate model[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2001, 18 (6): 1224- 1230.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-001-0036-y |
| 4 |
Gao X J , Xu Y , Zhao Z C , et al. On the role of resolution and topography in the simulation of East Asia precipitation[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2006, 86 (1): 173- 185.
doi: 10.1007/s00704-005-0214-4 |
| 5 |
Yu E T , Wang H J , Sun J Q . A quick report on a dynamical downscaling simulation over China using the nested model[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2010, 3 (6): 325- 329.
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2010.11446886 |
| 6 |
Gao X J , Wang M L , Giorgi F . Climate change over China in the 21st century as simulated by BCC_CSM1.1-RegCM4.0[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2013, 6 (5): 381- 386.
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2013.11447112 |
| 7 |
Zou L W , Zhou T J . Near future(2016-40)summer precipitation changes over China as projected by a regional climate model(RCM)under the RCP8.5 emissions scenario: comparison between RCM downscaling and the driving GCM[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 30 (3): 806- 818.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2209-x |
| 8 |
Xu Y , Xu C H . Preliminary assessment of simulations of climate changes over China by CMIP5 multi-models[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2012, 5 (6): 489- 494.
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2012.11447041 |
| 9 |
Dong S Y , Xu Y , Zhou B T , et al. Assessment of indices of temperature extremes simulated by multiple CMIP5 models over China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2015, 32 (8): 1077- 1091.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-015-4152-5 |
| 10 |
Nasrollahi N , AghaKouchak A , Cheng L Y , et al. How well do CMIP5 climate simulations replicate historical trends and patterns of meteorological droughts?[J]. Water Resources Research, 2015, 51 (4): 2847- 2864.
doi: 10.1002/2014WR016318 |
| 11 | 孙侦, 贾绍凤, 吕爱锋, 等. IPCC/AR5全球气候模式对1996-2005年中国气温模拟精度评价[J]. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34 (10): 1229- 1240. |
| 12 | 孙侦, 贾绍凤, 吕爱锋, 等. IPCC AR5全球气候模式模拟的中国地区日平均降水精度评价[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2016, 18 (2): 227- 237. |
| 13 | 韩振宇, 王宇星, 聂羽. RegCM4对中国东部区域气候模拟的辐射收支分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2016, 39 (5): 683- 691. |
| 14 | 韩振宇, 童尧, 高学杰, 等. 分位数映射法在RegCM4中国气温模拟订正中的应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (4): 331- 340. |
| 15 | 童尧, 高学杰, 韩振宇, 等. 基于RegCM4模式的中国区域日尺度降水模拟误差订正[J]. 大气科学, 2017, 41 (6): 1156- 1166. |
| 16 |
Han Z Y , Zhou B T , Xu Y , et al. Projected changes in haze pollution potential in China: an ensemble of regional climate model simulations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 17 (16): 10109- 10123.
doi: 10.5194/acp-17-10109-2017 |
| 17 | Shi Y , Wang G , Gao X J . Role of resolution in regional climate change projections over China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018, 51 (5): 2375- 2396. |
| 18 |
Zhang D , Han Z , Shi Y . Comparison of climate projections between driving CSIRO-Mk3.6.0 and downscaling simulation of RegCM4.4 over China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2017, 8 (4): 245- 255.
doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2017.10.001 |
| 19 | 高学杰, 赵宗慈, 丁一汇, 等. 温室效应引起的中国区域气候变化的数值模拟Ⅱ: 中国区域气候的可能变化[J]. 气象学报, 2003, 61 (1): 29- 38. |
| 20 | 高学杰, 徐影, 赵宗慈, 等. 数值模式不同分辨率和地形对东亚降水模拟影响的试验[J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30 (2): 185- 192. |
| 21 | 翟颖佳, 李耀辉, 徐影. RCPs情景下中国北方地区干旱气候变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35 (1): 94- 106. |
| 22 | 王若瑜, 谭云廷, 程炳岩, 等. 三峡库区气温变化高精度区域气候模式模拟与预估[J]. 气象科技, 2017, 45 (3): 469- 476, 491. |
| 23 |
Gao X J , Giorgi F . Use of the RegCM system over East Asia: review and perspectives[J]. Engineering, 2017, 3 (5): 766- 772.
doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.019 |
| 24 | Gao X J , Shi Y , Han Z Y . Performance of RegCM4 over major river basins in China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 34 (4): 441- 455. |
| 25 | Zhou B T , Wen Q H , Xu Y , et al. Projected changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in China by the CMIP5 multimodel ensembles[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27 (17): 6591- 6611. |
| 26 | Xu C H , Xu Y . The projection of temperature and precipitation over China under RCP scenarios using a CMIP5 multi-model ensemble[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2012, 5 (6): 527- 533. |
| 27 | Taylor K E . Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2001, 106 (D7): 7183- 7192. |
| 28 | 崔妍, 李倩, 周晓宇, 等. 5个全球气候模式对中国东北地区地面温度的模拟与预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2013, 29 (4): 37- 46. |
| 29 | 张姣艳, 李扬, 吴战平, 等. 贵州省未来气候变化(2018-2050年)预估分析[J]. 气象科技, 2018, 46 (6): 1165- 1171. |
| 30 | 张冬峰, 韩振宇, 石英. CSIRO-Mk3.6.0模式及其驱动下RegCM4.4模式对中国气候变化的预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13 (6): 557- 568. |
| 31 | 陶纯苇, 姜超, 孙建新. CMIP5模式对中国东北气候模拟能力的评估[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2016, 21 (3): 357- 366. |
| 32 | 姜燕敏, 吴昊旻. 20个CMIP5模式对中亚地区年平均气温模拟能力评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9 (2): 110- 116. |
| 33 | 敖雪, 翟晴飞, 崔妍, 等. CMIP5模式对东北地区气温模拟能力评估[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016, 28 (7): 105- 110. |
| 34 | 张艳武, 张莉, 徐影. CMIP5模式对中国地区气温模拟能力评估与预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12 (1): 10- 19. |
| 35 | 赵亚芳, 张宁, 陈燕, 等. 苏锡常地区热岛观测与数值模拟研究[J]. 气象科学, 2016, 36 (1): 80- 87. |
| 36 | 赵亮, 刘健, 靳春寒. CMIP5多模式集合对江苏省气候变化模拟评估及情景预估[J]. 气象科学, 2019, 39 (6): 739- 746. |
| 37 | 巩崇水, 段海霞, 李耀辉, 等. RegCM4模式对中国过去30a气温和降水的模拟[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33 (3): 379- 385, 394. |
| 38 | 朱涛. RegCM3.0与RegCM4.0对中国区域气候模拟的对比分析[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2012. |
| 39 | 陶纯苇, 姜超, 孙建新. CMIP5多模式集合对东北三省未来气候变化的预估研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59 (10): 3580- 3591. |
| 40 | 敖雪, 翟晴飞, 崔妍, 等. 东北地区气候变化CMIP5模式预估[J]. 气象科技, 2017, 45 (2): 298- 306, 312. |
| 41 | 胡芩, 姜大膀, 范广洲. CMIP5全球气候模式对青藏高原地区气候模拟能力评估[J]. 大气科学, 2014, 38 (5): 924- 938. |
| 42 | Zhou T J , Song F F , Chen X L . Historical evolution of global and regional surface air temperature simulated by FGOALS-s2 and FGOALS-g2:How reliable are the model results?[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 30 (3): 638- 657. |
| 43 | 李熠, 买苗. 基于全球及区域气候模式的江苏省降水变化趋势预估[J]. 大气科学学报, 2019, 42 (3): 447- 458. |
| 44 | 赵宗慈, 罗勇. 21世纪中国东北地区气候变化预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2007, 23 (3): 1- 4. |
| 45 | 周文翀, 韩镇宇. CMIP5全球气候模式对中国黄河流域气候模拟能力的评估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2018, 34 (6): 42- 55. |
| 46 | 王涛, 王乙舒, 沈玉敏, 等. CMIP5模式对辽宁省气温模拟能力及未来2℃升温阈值出现时间评估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (2): 49- 61. |
| [1] | Li CHEN,Shi-gong WANG,Gui-cai NING,Jin FAN,Jun-biao LIAN. Impact of a south branch trough in winter on heavy pollution process in southern Sichuan urban agglomeration [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(1): 9-15. |
| [2] | Xing-jie JI,Ya-lei DING,Feng-xiu LI,Xuan ZUO. Comparative analysis of the mean temperature trend before and after homogenization of the mean temperature data in He'nan province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(1): 43-52. |
| [3] | Wei JIN, Wei-hua LIU, Ling-feng GAO, Qian WANG, Guo-jing HAN. Research on the test and error correction in temperature forecasted by the ECWMF model in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 50-57. |
| [4] | Qian LI,Wan-ying ZHANG,Yi LIN,Yi-tong LIN,Xiao-yu ZHOU,Da-jun WANG,Rong LIN,Ling ZHU. Analysis of the climatic characteristics of warm winter in Liaoning province from 1961 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 68-73. |
| [5] | Qi YAN, Shuang LI, Fang-da TENG, Fang-ni WU, Shu-e LIANG, Ai-zhong ZHANG. Diagnoses of two foggy processes in Liaoning province in 2018 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 91-97. |
| [6] | Yu-hong LI,Su-lin TAO,Rong-ping LI,Lin-lin LI,Ting WANG,Bin ZHOU,Jing LI. Spatio-temporal evolution of vegetation coverage and its responses to climatic factors in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(5): 86-90. |
| [7] | Jie BAI,Zhi-ping FAN,Li-tao LIN,Qun LI,Xue-kai SUN,Xi-ping MA,Dan-dan LI. Temporal and spatial pattern of soil respiration pattern in urban green spaces of Shenyang [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(5): 105-112. |
| [8] | Nan ZHANG, Xiao-jun YANG, Qun-ying HE, Yi-wei LIU, Xiao-lei SUN. Analysis of mesoscale convection process of heavy rain in Tianjin caused by a typhoon remnant vortex [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(4): 1-10. |
| [9] | Yan-jing NIU, Xiang-jun XU, Huan GUO, Ming-ye LI. Verification of the short-term forecast of near-surface temperature using different global forecast products in China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(4): 18-27. |
| [10] | Jing XU. Relationship between near-surface ozone concentration and temperature in Qinhuangdao [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(4): 83-88. |
| [11] | Ling-ling JI,Zhu-xiang XI,Zhuo CHEN,Yu-xi LIU. Study on climatic characteristics and assessment methods of high temperature weather in Jilin province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(3): 49-54. |
| [12] | Xiu-juan WANG, Zhong-bao JIANG, Xiao-hua MA, Xu FENG. Causes analysis of heavy rainfall in 2018 in Jilin province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(2): 1-8. |
| [13] | Xu FAN,Ying HUANG,Wen-nan LENG,Bei-dou ZHANG,Wen-yu ZHANG,Guo-yin WANG. Inversion of ground-based microwave radiometer measurements using radial basis function neural network [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(2): 62-69. |
| [14] | LI Shang-feng, GAO Zong-ting, YANG Xu, YIN Lu-ting. Characteristics of temperature decline between two adjacent days and its interdecadal change during winter in Northeast China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(6): 77-84. |
| [15] | DU Qi-cheng, HUANG Jun-kai, SHEN Xu-yang, NIU Jun-yi. Climate characteristics of high-temperature and diagnosis of a continuous high-temperature process in Huangshan area [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(6): 85-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|