国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 115-123.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2024.03.014
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Meiyan ZHAO1( ),Jun ZHU1,Jun YU2,Zhen JIANG3
),Jun ZHU1,Jun YU2,Zhen JIANG3
Received:2022-11-01
Online:2024-06-28
Published:2024-08-09
CLC Number:
Meiyan ZHAO,Jun ZHU,Jun YU,Zhen JIANG. Application assessment of wind profiler radar data in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 115-123.
Table 1
Statistical comparisons of the L-band radiosonde observations and wind profiler radar measurements to the corresponding ERA5 reanalysis data"
| 统计量 | u | v | |||||
| RRM | Δ${\bar X}$(m·s-1) | StdΔX(m·s-1) | RRM | Δ${\bar X}$(m·s-1) | StdΔX(m·s-1) | ||
| 探空资料 | 0.84 | -0.01 | 2.16 | 0.86 | -0.14 | 2.32 | |
| 风廓线资料 | 0.72 | 0.19 | 3.26 | 0.6 | 0.01 | 3.84 | |
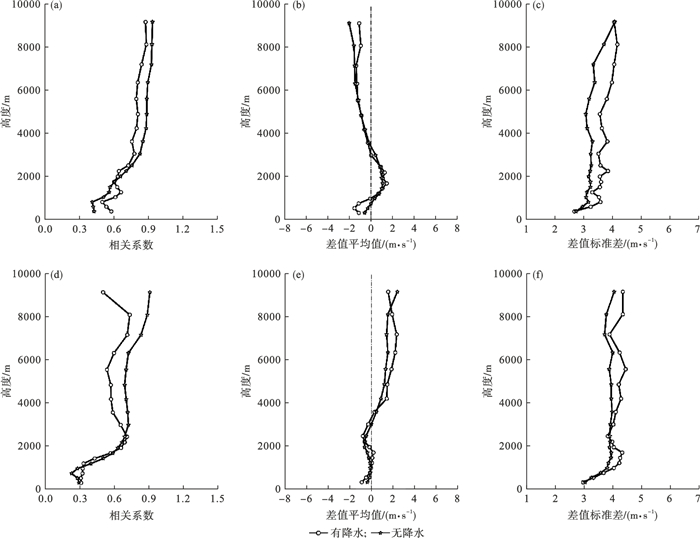
Fig.4
Variation of correlation coefficients (a, d), averaged differences (b, e), and difference standard deviations (c, f) between the wind profile radar measurements and the ERA5 reanalysis data under different weather conditions towards the u-component (a, b, c) and v-component (d, e, f) winds"
| 1 |
易仕明, 陈奕隆. 观测高空风的新装备——风廓线雷达[J]. 气象, 1988, 14 (11): 3- 8.
doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.1988.11.001 |
| 2 | 胡明宝. 风廓线雷达探测与应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2015: 1. |
| 3 | 顾映欣, 陶祖钰. UHF多普勒风廓线雷达资料的初步分析和应用[J]. 气象, 1991, 17 (1): 29- 34. |
| 4 | 翟亮. 北京奥运期间一次暴雨过程风廓线资料特征[J]. 气象, 2008, 34 (S1): 26- 31. |
| 5 |
刘莲, 王迎春, 陈明轩. 京津冀一次飑线过程的精细时空演变特征分析[J]. 气象, 2015, 41 (12): 1433- 1446.
doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2015.12.001 |
| 6 | 梁寒, 阎琦, 李爽, 等. 2019年沈阳一次凌晨气温骤升过程成因精细分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2022, 38 (3): 45- 51. |
| 7 | 马梁臣, 马洪波, 张曦丹, 等. 冬奥会张家口赛区一次降水相态特征分析[J]. 气象与环境报, 2022, 38 (1): 1- 7. |
| 8 | 康雪, 许晨, 张恬月. 不同降水强度下风廓线雷达谱矩特征与测风准确性分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2020, 40 (3): 90- 95. |
| 9 | 邓闯, 阮征, 魏鸣, 等. 风廓线雷达测风精度评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23 (5): 523- 533. |
| 10 | 李晨光, 刘淑媛, 陶祖钰. 华南暴雨试验期间香港风廓线雷达资料的评估[J]. 热带气象学报, 2003, 19 (3): 269- 276. |
| 11 | 董保举, 张晔, 徐安伦, 等. 风廓线雷达测风和气球测风资料对比分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33 (S1): 18- 25. |
| 12 | 吴蕾, 陈洪滨, 康雪. 风廓线雷达与L波段雷达探空测风对比分析[J]. 气象科技, 2014, 42 (2): 225- 230. |
| 13 | 王栋成, 邱粲, 曹洁, 等. 济南边界层风廓线雷达与L波段雷达探空测风资料对比研究[J]. 气象科学, 2018, 38 (3): 416- 422. |
| 14 | 王栋成, 邱粲, 董旭光, 等. 济南边界层风廓线雷达与L波段雷达大风探空测风对比[J]. 气象, 2019, 45 (8): 1169- 1180. |
| 15 | 王欣, 卞林根, 彭浩, 等. 风廓线仪系统探测试验与应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2005, 16 (5): 693- 698. |
| 16 | 孙旭映, 韩晖, 段海霞, 等. 风廓线仪与气球测风资料的对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2008, 26 (3): 48- 52. |
| 17 | 万蓉, 周志敏, 崔春光, 等. 风廓线雷达资料与探空资料的对比分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2011, 30 (2): 130- 136. |
| 18 | Graham R M , Hudson S R , Maturilli M . Improved performance of ERA5 in Arctic gateway relative to four global atmospheric reanalyses[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46 (11): 6138- 6147. |
| 19 | Hersbach H , Bell B , Berrisford P , et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2020, 146 (730): 1999- 2049. |
| 20 | Wang C X , Graham R M , Wang K G , et al. Comparison of ERA5 and ERA-Interim near-surface air temperature, snowfall and precipitation over Arctic sea ice: Effects on sea ice thermodynamics and evolution[J]. The Cryosphere, 2019, 13 (6): 1661- 1679. |
| 21 | 刘鸿波, 董理, 严若婧, 等. ERA5再分析资料对中国大陆区域近地层风速气候特征及变化趋势再现能力的评估[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2021, 26 (3): 299- 311. |
| 22 | 谭海燕, 邵珠晓, 梁丙臣, 等. ERA5风场与NCEP风场在黄海、东海波浪模拟的适用性对比研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2021, 40 (5): 524- 540. |
| 23 | 李伟, 刘凤琴, 徐磊, 等. L波段高空气象探测系统软件[J]. 气象科技, 2008, 36 (2): 237- 239. |
| 24 | 赵兴炳, 李跃清. 风廓线雷达原理及其在高原地区探测结果初析[J]. 四川气象, 2006, 26 (2): 24- 26. |
| 25 | 胡明宝, 张鹏. 风廓线雷达测量性能分析[J]. 气象科技, 2011, 39 (3): 315- 319. |
| 26 | 廖菲, 邓华, 侯灵. 降水条件下风廓线雷达数据质量分析及处理[J]. 热带气象学报, 2016, 32 (5): 588- 596. |
| 27 | 陈树成, 李晓波, 崔明, 等. 不同天气条件下微波辐射计和风廓线雷达探测数据误差特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37 (1): 67- 72. |
| [1] | Xiaolong HUANG,Xiaoming XIANG,Liwei WANG,Shiying LI,Yuhe JIANG. Research on the applicability of IMERG satellite retrieval and ERA5 land reanalysis precipitation products in Sichuan region, China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 65-75. |
| [2] | Tao WANG, Yi-shu WANG, Chun-yu ZHAO, Xiao-tao WANG, Mei-ou QIN, Yu-min SHEN, Yi-ling HOU, Jian-yun ZHAO. Prediction model of first-frost date in Liaoning province using machine learning methods [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(4): 47-56. |
| [3] | An-ke GUO,Xiao-ge YIN,Zhi-min WANG,Zhi-qiang LI,Zhe LI,Ji ZHANG,Lu CHEN,Hao-yun HUANG. A study on the response relationship between air pollution process and meteorological wind field in an industrial park [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(1): 23-32. |
| [4] | Xing ZHI,Jian-guo TAN,Lan-dong SUN. Characteristics of upper-level air temperature over East China from 1961 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(2): 48-55. |
| [5] | Shu-cheng CHEN,Xiao-bo LI,Ming CUI,Yan WANG. Error analysis of detection data of microwave radiometer and wind profiler radar under different weather conditions [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(1): 67-72. |
| [6] | JIN Chen-xi, GUO Wen-li, GAN Lu, WANG Chun-ling. Statistics and possible sources of low-level turbulence below 3000 m and its meteorological condition in Beijing [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(5): 18-26. |
| [7] | MENG Ying-ying, CAO Dian-bin, WU Yan, WANG Zi-yang. Comparisons of dynamic downscaling of the wind field in forest areas of Da-Xiao-Xing'anling Mountains [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(4): 8-15. |
| [8] | CHENG Hu-hua, WANG Yi-bai, WEN Bin, WU Shuai, ZHI Mao-lin, ZHAO Liang. Confidence analysis of rainy and snowy weather diagnosis in Kelan,Shanxi province based on NCEP FNL data [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(2): 23-31. |
| [9] | CHENG Pan, SUN Hong-yu, CHEN Chuan-lei, CAI Kui-zhi, WANG Shu-yao, XIAO Guang-liang, LIU Jing, CHENG Hang, WANG Yi-wen. Application of high-frequency ground wave radar in early warning of sea gale in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(5): 25-34. |
| [10] | SHEN Yang, SHEN An-yun, SU Hang, XIONG Shi-wei, YAN Wen-lian. Causes analysis on a large-range dense fog event in the winter of 2016 over Jiangsu province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(4): 11-20. |
| [11] | ZHANG Wen-jing HU Lin WU Su-liang WANG Qi TIAN Liang . Characteristics of haze and clean weather and their influencing factors in Xi'an [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2015, 31(2): 31-36. |
| [12] | ZHI Xing,XU Hai-ming,MI Wei-hong,SU Zhi-xia,DUAN Xiang-suo,TANG Zhen-xing. Comparative analysis of atmospheric temperature between three reanalysis datasets and radiosonde dataset in northeast and northwest of China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(6): 147-157. |
| [13] | LU Huan-zhen, LIU Yi-wei, ZHANG Nan. Cause of heavy rain by shear line in the Haihe river basin [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(1): 15-22. |
| [14] | CHEN Zhe,GAO Jie, YANG Xu . Introduction of IGRA dataset and analysis of its data quality [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(5): 106-111. |
| [15] | HU Hao-li,WANG Cheng-wei. Forming reason of a rare rainstorm on July of 2011 in the west of Heilongjiang province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2013, 29(3): 15-20. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|