国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 11-18.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2022.04.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue YU1,2( ),Ming-lin BI3,Qi YAN1,2,*(
),Ming-lin BI3,Qi YAN1,2,*( ),Hai-feng LIN2,Dong-lei FENG2,Fan-yue YU2
),Hai-feng LIN2,Dong-lei FENG2,Fan-yue YU2
Received:2021-12-13
Online:2022-08-28
Published:2022-09-22
Contact:
Qi YAN
E-mail:592398487@qq.com;yq.mete@163.com
CLC Number:
Yue YU, Ming-lin BI, Qi YAN, Hai-feng LIN, Dong-lei FENG, Fan-yue YU. Cause analysis and spatial test of multi-mode numerical prediction on regional rainstorms in Liaoning province[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(4): 11-18.
Table 2
Classification of regional rainstorms in 2020 in Liaoning areas"
| 暴雨分型 | 发生时段 | 影响系统 | 平均雨量/mm | 最大小时雨量/mm | 最大累计雨量/mm |
| 气旋型 | 5.18—5.19 | 江淮气旋、东北冷涡 | 24.0 | 30.6 | 86.9 |
| 8.15—8.16 | 华北气旋、东北冷涡 | 14.2 | 53.6 | 165.2 | |
| 冷涡型 | 8.03—8.04 | 东北冷涡 | 15.5 | 80.7 | 134.0 |
| 8.18—8.19 | 东北冷涡、切变线 | 31.0 | 71.8 | 221.3 | |
| 8.23—8.24 | 高空槽、东北冷涡 | 11.2 | 51.7 | 135.3 | |
| 9.15—9.16 | 东北冷涡 | 19.6 | 50.1 | 120.7 | |
| 5.21—5.24 | 东北冷涡 | 31.9 | 29.0 | 98.6 | |
| 9.05—9.06 | 东北冷涡、高空槽、低层切变线、低空急流 | 4.9 | 72.1 | 82.0 | |
| 台风型 | 8.05—8.06 | 4号“黑格比” | 5.7 | 44.2 | 112.9 |
| 8.25—8.28 | 8号“巴威” | 41.4 | 71.7 | 202.7 | |
| 9.07—9.08 | 10号“海神” | 12.5 | 21.4 | 83.0 | |
| 9.02—9.03 | 9号“美莎克” | 16.5 | 47.1 | 96.9 |
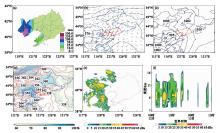
Fig.2
Observed 24 h rainfall at 08:00 on July 13 (a), geopotential height at 500 hPa and wind field at 850 hPa at 20:00 (b), sea level pressure at 20:00 (c), equivalent potential temperature and relative humidity at 850 hPa at 20:00 (d), radar reflectivity factor at 17:00 (e), vertical section of time evolution of reflectivity factor along the location (119.78°E, 41.79°N) (f) on July 12, 2021"
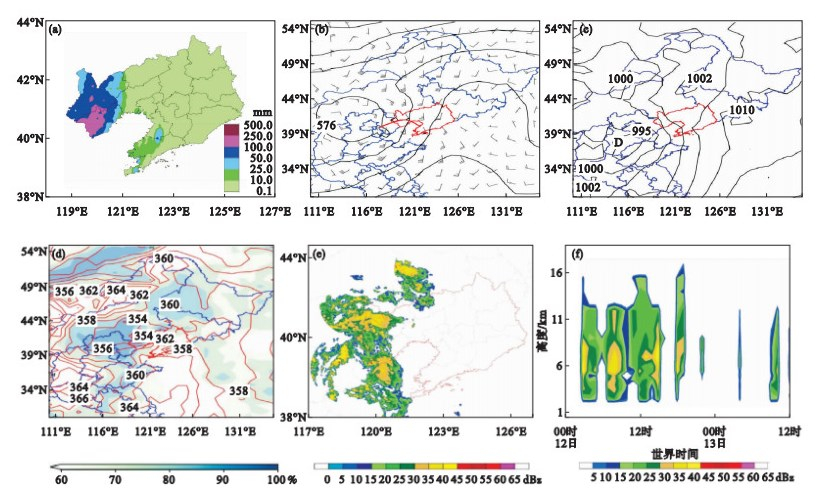
Fig.3
Observed rainfall from 17:00 on July 13 to 20:00 on July 14 (a), geopotential height at 500 hPa and wind field at 850 hPa at 20:00 (b), sea level pressure at 20:00 (c), equivalent potential temperature and relative humidity at 850 hPa at 20:00 (d), radar reflectivity factor at 18:00 (e), vertical section of time evolution of reflectivity factor along the location (123.13°E, 40.48°N) (f) on July 13, 2021"
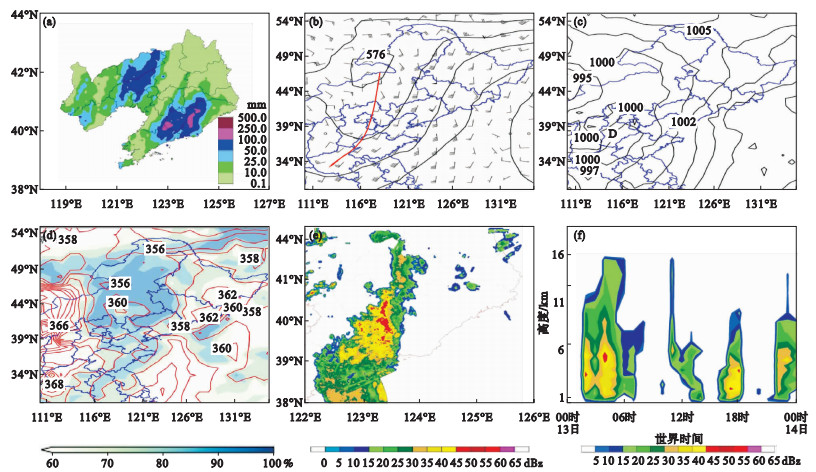
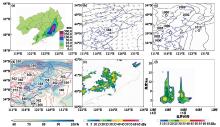
Fig.4
Observed precipitation in the past 12-h at 08:00 on July 15 (a), geopotential height at 500 hPa and wind field at 850 hPa at 20:00 (b), sea level pressure at 20:00 (c), equivalent potential temperature and relative humidity at 850 hPa at 20:00 (d), radar reflectivity factor at 21:00 (e), vertical section of time evolution of reflectivity factor along the location (123.00°E, 40.21°N) (f) on July 14, 2021"
| 1 | 李勇, 王雨. 2007年夏季CMA-MESO15及30km模式对比检验[J]. 气象, 2008, 34 (10): 81- 89. |
| 2 | 熊秋芬. CMA_Meso模式的降水格点检验和站点检验分析[J]. 气象, 2011, 37 (2): 185- 193. |
| 3 | 张建海, 诸晓明. 数值预报产品和客观预报方法预报能力检验[J]. 气象, 2006, 32 (2): 58- 63. |
| 4 | 聂安祺, 李得勤, 滕方达, 等. 辽宁省夏季多模式降水预报检验及晴雨预报技术研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (5): 10- 17. |
| 5 | 张旭, 孙宝利, 白佳宁, 等. 阜新地区东北冷涡多模式降水预报检验[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37 (3): 19- 24. |
| 6 | 张博, 赵滨, 牛若芸, 等. 全球模式对华北区域性强降水中期预报能力检验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36 (2): 118- 124. |
| 7 | 李子良, 赵滨, 李国平. 邻域空间检验技术在集合降水预报检验中的应用[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44 (2): 189- 198. |
| 8 | 陈涛, 陈博宇, 于超, 等. 华南前汛期锋面对流系统和暖区对流系统的多尺度特征和集合预报敏感性对比分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46 (9): 1129- 1142. |
| 9 | 公颖. SAL定量降水预报检验方法的解释与应用[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2010, 29 (2): 153- 159. |
| 10 | 金小霞, 俞剑蔚, 刘梅, 等. 基于SAL方法对一次区域性大暴雨过程多模式预报空间检验及误差分析[J]. 气象科学, 2020, 40 (6): 791- 801. |
| [1] | Yun-xia DUAN,De-qin LI,Yong-ming JI,Wei-long BAN,Yu-tong WU,Xiao-ou LI. Analysis of strong precipitation in the urban area of Shenyang under the Northeast Cold Vortex background [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(4): 1-10. |
| [2] | Hui-meng BAO,Da-feng GUO,Wei LI. Correction tests of ECMWF modeling quantitative precipitation using frequency matching method in Jiangxi provice [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(2): 12-20. |
| [3] | Qi XUE,Ya-ping TANG,Li-na WANG,Hai-feng GUO,Hui ZHAO,Peng-cheng MA. Spatiotemporal distribution of short-term heavy precipitation and characteristics of synoptic condition during summer in Pingliang, Gansu province from 2015 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(1): 57-64. |
| [4] | Yao HUANG,Jia-xing YOU,Tian-gui XIAO,Jie GUO. Effects of low-frequency oscillation on the persistent extreme precipitation in Western Sichuan [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(3): 47-56. |
| [5] | ZHENG Shi, WANG Guan, LIN Zhong-guan, GUAN Jian-hua, HUANG Xing-you. Characteristics analysis of heavy precipitation in China from 1961 to 2013 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(6): 102-107. |
| [6] | LIU Lei, ZHOU Jing, LIU Jun-jie, GAO Hui. Decadal characteristics of persistent heavy precipitation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its circulation pattern [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(3): 28-36. |
| [7] | ZHANG Duan-yu, CUI Chun-guang, XU Ming, WANG Jing-yu, HU Chang-qiong. Analysis of the evolution of convective clouds during a rainstorm in 2015 over Hubei province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(2): 8-17. |
| [8] | SHEN Cheng,YAN Ting-bai,LIU Dong-qing,LI Jing2. Characteristics of short-time heavy precipitation from 2008 to 2012 in Nanjing [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2015, 31(1): 28-33. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jing,YAO Wen,HE Xiao-dong,WU Fu-jie,ZHAO Xiao-chuan, WANG Dong. Study on quantitative test and forecast index of numerical forecast precipitation products in Yingkou region [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(1): 30-35. |
| [10] | ZHAO Jun-rong. Analysis of meso-micro scale system in a?rare heavy rain on the?northern slope of Tianshan Mountain [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2012, 28(6): 19-24. |
| [11] | ZHOU Xiao-shan CUI Jin WANG Lian-zhong CHEN Li-qiang YANG Sen. Establishment of numerical prediction system for Northeast China cold vortex and its operational application [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2012, 28(5): 1-. |
| [12] | ZHANG Ning-na,HUANG Ge, WU Man-li,LIANG Han,SHENG Yong,LIU Gui-ying. Contrastive verification of three numerical prediction products in the northeast of China in 2010 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2012, 28(2): 28-34. |
| [13] | WANG Hong, FENG Hong-Fang, SHI Yu, SUI Ping, YU Yong-Jiang. Forecasting verification of CAPPS3 mode in Fuzhou, Fujian province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2011, 27(4): 25-29. |
| [14] | YANG Hong-bin;ZOU Xu-dong;ZHANG Yun-hai;WANG Hong-yu;LIU Yu-che. Background value problems in SO2 urban air pollution numerical prediction [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2010, 26(5): 69-72. |
| [15] | CHEN Chuan-lei;WU Xiao-feng;SUN Xiao-wei;WANG Ying;WANG Tai-wei;WEI Xiao-lin. Climatic characteristics of severe convective weather in Liaoning province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2010, 26(3): 27-33. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|