国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 51-60.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2023.06.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Miao WANG1( ),Pengcheng QIN1,Chenxu SHE2,Xiaofang ZHAO1,Mingwei YANG3
),Pengcheng QIN1,Chenxu SHE2,Xiaofang ZHAO1,Mingwei YANG3
Received:2022-03-11
Online:2023-12-28
Published:2024-01-27
CLC Number:
Miao WANG, Pengcheng QIN, Chenxu SHE, Xiaofang ZHAO, Mingwei YANG. Simulation and projection of climate change in Central China based on CMIP6 multi-model ensemble[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(6): 51-60.
Table 1
Basic information of 12 CMIP6 models"
| 序号 | 模式 | 国家 | 分辨率/(纬度°×经度°) | 情景 | 历史时间/预估时间 |
| 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | 澳大利亚 | 1.2°×1.8° | HIS/126/245/370/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 2 | ACCES-ESM1-5 | 澳大利亚 | 1.2°×1.8° | HIS/126/245/370/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 3 | BCC-CSM2-MR | 中国 | 1.1°×1.1° | HIS/126/245/370/585 | 1961—2014年/2005—2100年 |
| 4 | CCCma-CanESM5 | 加拿大 | 2.8°×2.8° | HIS/126/245/370/585 | 1961—2014年/2005—2100年 |
| 5 | CNRM-CM6-1 | 法国 | 1.4°×1.4° | HIS/126/245/370/585 | 1850—2014年/2005—2100年 |
| 6 | Hadgem3-gc31-LL | 英国 | 1.3°×1.9° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 7 | INM-CM4-8 | 俄罗斯 | 1.5°×2.0° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 8 | INM-CM5-0 | 俄罗斯 | 1.5°×1.5° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 9 | IPSL-CM6A-LR | 法国 | 1.3°×2.5° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 10 | MIROC6 | 日本 | 1.4°×1.4° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 11 | MPI-ESM1-2-HR | 德国 | 0.9°×0.9° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
| 12 | MRI-ESM2-0 | 德国 | 1.1°×1.1° | HIS/126/245/585 | 1901—2014年/2015—2100年 |
Table 2
Spatial simulation results for temperature and precipitation in Central China from 1961 to 2014 using 12 CMIP6 models"
| 序号 | 模式 | 气温 | 降水 | |||||
| 空间相关系数 | 标准差比 | 均方根误差/℃ | 空间相关系数 | 标准差比 | 均方根误差/mm | |||
| 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | 0.84* | 1.27* | 0.04* | 0.98 | 0.96 | 3.51 | |
| 2 | ACCES-ESM1-5 | 0.82 | 1.26 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 1.93 | |
| 3 | BCC-CSM2-MR | 0.83* | 1.25* | 0.05* | 0.98 | 1.16 | 7.62 | |
| 4 | CCCma-CanESM5 | 0.83 | 1.29 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 3.34 | |
| 5 | CNRM-CM6-1 | 0.84* | 1.29* | 0.05* | 0.98* | 1.01* | 2.61* | |
| 6 | Hadgem3-gc31-Ⅱ | 0.84* | 1.26* | 0.05* | 0.98 | 0.97 | 3.83 | |
| 7 | INM-CM4-8 | 0.84 | 1.28 | 0.05 | 0.98* | 0.97* | 2.24* | |
| 8 | INM-CM5-0 | 0.83* | 1.28* | 0.05* | 0.98 | 1.04 | 2.15 | |
| 9 | IPSL-CM6A-LR | 0.83 | 1.28 | 0.04 | 0.97* | 0.93* | 2.70* | |
| 10 | MIROC6 | 0.82* | 1.26* | 0.05* | 0.98* | 1.02* | 2.89* | |
| 11 | MPI-ESM1-2-HR | 0.85 | 1.32 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 2.46 | |
| 12 | MRI-ESM2-0 | 0.84 | 1.28 | 0.55 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 4.64 | |
| 优选模式集合平均 | 0.84 | 1.26 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 2.22 | ||
Table 3
Projections of temperature and precipitation in Central China for different future periods under three scenarios from 2021 to 2100 simulated by an ensemble of optimally selected CMIP6 models"
| 气象要素 | 情景 | 2021—2100年 | 近期 | 中期 | 远期 |
| 气温/(℃/10 a) | SSP1-2.6 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 0.28 | -0.06 |
| SSP2-4.5 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.15 | |
| SSP5-8.5 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.75 | |
| 降水/(mm/10 a) | SSP1-2.6 | 16.2 | -18.3 | -3.9 | 39.5 |
| SSP2-4.5 | 12.3 | 10.8 | 40.6 | -0.6 | |
| SSP5-8.5 | 19.3 | 6.2 | 4.3 | -14.1 |
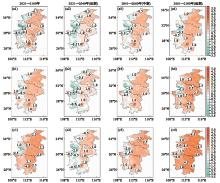
Fig.5
Simulations of the annual mean temperature anomalies from six preferentially selected CMIP6 model ensembles (relative to the baseline period of 1995-2014) under the SSP1-2.6 (a), SSP2-4.5 (b), SSP5-8.5 (c) scenarios for Central China, for the years 2021-2100, the near-term period of 2021-2040 (near period), the mid-term period of 2041-2060 (mid period), and the long-term period of 2081-2100(end period)"
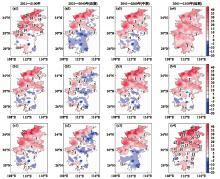
Fig.6
Simulations of the annual mean precipitation anomalies from six preferentially selected CMIP6 model ensembles (relative to the baseline period of 1995-2014) under the SSP1-2.6 (a), SSP2-4.5 (b), SSP5-8.5 (c) scenarios for Central China, for the years 2021-2100, the near-term period of 2021-2040 (near period), the mid-term period of 2041-2060 (mid period), and the long-term period of 2081-2100 (end period)"
Table 4
Statistical comparisons of temperature and precipitation simulations between CMIP5 and CMIP6 models for different future periods in Central China"
| 统计量 | 情景 | 未来 | 近期 | 中期 | 远期 |
| 气温变幅/℃ | SSP2-4.5 | 1.29 | 0.34 | 1.01 | 2.14 |
| RCP4.5 | 2.08 | 1.13 | 2.07 | 2.88 | |
| 气温变化趋势/(℃/10 a) | SSP2-4.5 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.15 |
| RCP4.5 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.46 | -0.11 | |
| 降水变率/(%) | SSP2-4.5 | 6.85 | 3.24 | 8.62 | 8.67 |
| RCP4.5 | 2.79 | 2.73 | -1.86 | 7.58 | |
| 降水变化趋势/(mm/10 a) | SSP2-4.5 | 12.3 | 10.8 | 40.6 | -0.6 |
| RCP4.5 | 7.71 | -21.13 | 18.19 | 35.00 |
| 1 | 秦大河. 气候变化科学与人类可持续发展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33 (7): 874- 883. |
| 2 | 姜大膀, 富元海. 2 ℃全球变暖背景下中国未来气候变化预估[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36 (2): 234- 246. |
| 3 | 姜江, 姜大膀, 林一骅. RCP4.5情景下中国季风区及降水变化预估[J]. 大气科学, 2015, 39 (5): 901- 910. |
| 4 | 阮甜, 查芊郁, 杨茹, 等. 全球升温1.5 ℃和2.0 ℃对长江寸滩站以上流域径流的影响[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28 (2): 407- 415. |
| 5 | 李东欢, 邹立维, 周天军. 全球1.5 ℃温升背景下中国极端事件变化的区域模式预估[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32 (4): 446- 457. |
| 6 | 翟盘茂, 周佰铨, 陈阳. 气候变化科学方面的几个最新认知[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (6): 629- 635. |
| 7 | 周天军, 陈梓明, 陈晓龙, 等. IPCC AR6报告解读: 未来的全球气候——基于情景的预估和近期信息[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (6): 652- 663. |
| 8 | 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 从检验CMIP5气候模式看CMIP6地球系统模式的发展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (6): 643- 648. |
| 9 | 张丽霞, 陈晓龙, 辛晓歌. CMIP6情景模式比较计划(ScenarioMIP)概况与评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15 (5): 519- 525. |
| 10 | 姜彤, 吕嫣冉, 黄金龙. CMIP6模式新情景(SSP-RCP)概述及其在淮河流域的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10 (5): 102- 109. |
| 11 | 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. CMIP6的设计[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12 (3): 258- 260. |
| 12 | 周天军, 邹立维, 陈晓龙. 第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6)评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15 (5): 445- 456. |
| 13 |
Fu Y H , Lin Z D , Guo D . Improvement of the simulation of the summer East Asian westerly jet from CMIP5 to CMIP6[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2020, 13 (6): 550- 558.
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2020.1746175 |
| 14 | 魏萌, 舒启, 宋振亚, 等. CMIP6气候模式对21世纪初全球增暖减缓现象模拟能力评估与归因分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51 (6): 947- 961. |
| 15 |
Zhu H H , Jiang Z H , Li J , et al. Does CMIP6 inspire more confidence in simulating climate extremes over China?[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 37, 1119- 1132.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-9289-1 |
| 16 |
Chen H P , Sun J Q , Lin W Q , et al. Comparison of CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating climate extremes[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65 (17): 1415- 1418.
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.05.015 |
| 17 | 王予, 李惠心, 王会军, 等. CMIP6全球气候模式对中国极端降水模拟能力的评估及其与CMIP5的比较[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79 (3): 369- 386. |
| 18 | 胡一阳, 徐影, 李金建, 等. CMIP6不同分辨率全球气候模式对中国降水模拟能力评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (6): 730- 743. |
| 19 |
Xin X G , Wu T W , Zhang J , et al. Comparison of CMIP6 and CMIP5 simulations of precipitation in China and the East Asian summer monsoon[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2020, 40 (15): 6423- 6440.
doi: 10.1002/joc.6590 |
| 20 |
Lin W Q , Chen H P . Assessment of model performance of precipitation extremes over the mid-high latitude areas of Northern Hemisphere: from CMIP5 to CMIP6[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2020, 13 (6): 598- 603.
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2020.1820303 |
| 21 | 赵梦霞, 苏布达, 姜彤, 等. CMIP6模式对黄河上游降水的模拟及预估[J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40 (3): 547- 558. |
| 22 | 李纯, 姜彤, 王艳君, 等. 基于CMIP6模式的黄河上游地区未来气温模拟预估[J]. 冰川冻土, 2022, 44 (1): 171- 178. |
| 23 | 姜彤, 吕嫣冉, 黄金龙, 等. CMIP6模式新情景(SSP-RCP)概述及其在淮河流域的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10 (5): 102- 109. |
| 24 | 李晓蕾, 王卫光, 张淑林. 基于CMIP6多模式的长江流域未来降水变化趋势分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2022, 3, 1-7, 12. |
| 25 | 王慧, 肖登攀, 赵彦茜, 等. 基于CMIP6气候模式的华北平原极端气温指数评估和预测[J]. 2021, 37(5): 86-94, 142. |
| 26 | 黄子立, 吴小飞, 毛江玉. CMIP6模式水平分辨率对模拟我国西南地区夏季极端降水的影响评估[J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40 (6): 1470- 1483. |
| 27 | 崔讲学. 华中区域气候变化评估报告: 2012[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2014. |
| 28 | 刘敏, 王凯, 万素琴, 等. 华中区域气候变化评估报告: 2020[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2021. |
| 29 | 任永建, 万素琴, 肖莺, 等. 华中区域气温变化的模拟评估及未来情景预估[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70 (5): 1098- 1106. |
| 30 |
王苗, 刘敏, 任永建. 基于高分辨率模拟数据RCP4.5情景下的华中区域气候变化预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37 (3): 65- 72.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2021.03.009 |
| 31 |
Qin P C , Xu H M , Liu M , et al. Projected impacts of climate change on major dams in the Upper Yangtze River Basin[J]. Climate Change, 2022, 170, 8.
doi: 10.1007/s10584-021-03303-w |
| 32 | 刘绿柳, 魏麟骁, 徐影, 等. 气候变化对黄河流域生态径流影响预估[J]. 水科学进展, 2021, 32 (6): 824- 833. |
| 33 |
王涛, 王乙舒, 沈玉敏, 等. CMIP5模式对辽宁省气温模拟能力及未来2 ℃升温阈值出现时间评估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36 (2): 49- 61.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2020.02.007 |
| 34 |
Torrence C , Compo G P . A practical guide to wavelet analysis[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorogical Society, 1998, 79 (1): 61- 78.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0061:APGTWA>2.0.CO;2 |
| 35 | 周莉, 兰明才, 蔡荣辉, 等. 21世纪前期长江中下游流域极端降水预估及不确定性分析[J]. 气象学报, 2018, 76 (1): 47- 61. |
| 36 | 邓荔, 朱欢欢, 江志红. 不同情景达到碳中和下中国区域气候变化的预估[J]. 大气科学学报, 45 (3): 364- 375. |
| 37 | 石英, 高学杰, 吴佳, 等. 华北地区未来气候变化的高分辨率数值模拟[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21 (5): 580- 589. |
| 38 |
王涛, 王乙舒, 崔妍, 等. 气候模式对东北三省降水模拟能力评估及预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2016, 32 (5): 52- 60.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2016.05.008 |
| [1] | HUANG Xiaolong, XIANG Xiaoming, WANG Liwei, LI Shiying, JIANG Yuhe. Research on the applicability of IMERG satellite retrieval and ERA5 land reanalysis precipitation products in Sichuan region,China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 65-75. |
| [2] | LI Ying, YU Changwen, XU Kang. Analysis of precipitation variability characteristics in Hebei province and the impact factors during 1961-2021 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 91-96. |
| [3] | SONG Yang, WANG Ji, FENG Puyu, XU Liping, WANG Feng, ZHANG Wei, TANG Xiru, WANG Bin. Characteristics and impact analysis of extreme climate events in Beijing-Tianjin- Hebei region based on ETCCDI indices [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 97-105. |
| [4] | DAWA Ciren, LUO Zhui, HONG Yihang, CIREN Zhuoga. Impact of aerosol on rainy season precipitation in Xizang Plateau based on machine learning method [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(3): 138-144. |
| [5] | Qingyuan GAO,Wei JIN,Qingquan GAO,Qingzhe XU,Lu TIAN,Dongxia LIU,Guojing HAN. Diagnostic analysis of the extreme rain-snow process in Liaoning province from November 7-9, 2021 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 1-8. |
| [6] | Dongnan LI,Qiannan GAO,Guozhi SUN,Pengfei SUN,Ximing ZHANG,Qiang XIA. Spatiotemporal distribution of precipitation in Heilongjiang province from 1991 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 17-25. |
| [7] | Yue CAO,Weimiao QIAN,Guocui LI,Yang FENG,Tong GAO. Characteristics of fine-scale distribution of short-term heavy precipitation over the central and southern regions of Hebei province in summers from 2013 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 26-33. |
| [8] | Huosheng LIU,Jiahui ZAN,Yatian CHENG,Qianhui YU,Changguang WU. Analysis of spatiotemporal variations in air temperature among three types of spaces in Wuhan city during the summer of 2022 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 51-58. |
| [9] | Lin CHENG,Yaojie HAN,Chengda HU. Analysis of meteorological indicators for grain quality evaluation of winter wheat in He'nan province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(2): 69-76. |
| [10] | Gongmei CHEN,Ruixiao LI,Hailing HUANG,Houzhi LUO. Characteristics and causes of heavy precipitation differences at Wenzhou Airport caused by typhoon "Hagupit" and "Lekima" [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(1): 9-16. |
| [11] | Feifan LIU,Yongguang ZHENG,Ran LUO. Synoptic patterns and characteristics of environmental parameters for early-morning heavy rainfall over Beijing, Tianjin, and most of Hebei Plains [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(1): 17-26. |
| [12] | Xiaoxuan SU,Xiaowei SUN,Chenhe ZHANG,Jia-qi LI,Zengxin LU,Xu YANG. Application and verification of the spatiotemporal projection model in the extended-range forecast of summer precipitation in Northeast China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(1): 27-36. |
| [13] | Hao QIN,Fengqin ZHENG,Chongzhi SUN. The impact of winter sea surface temperature change in the central eastern tropical Pacific on the number of heavy fog days in Guangxi [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(1): 79-87. |
| [14] | Mian LIANG, Liujie PAN, Bei JIA, Wenlian YAN, Tianshu WANG, Xingxing GAO, Peirong LI. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of explosive intensification of a persistent heavy fog event over Guanzhong Plain, Shaanxi in January 2019 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(6): 18-27. |
| [15] | Yue WANG,Chenghan LIU,Yunxia DUAN,Hongyu SUN,Jinglin CUI,Yumeng SU,Peiyu CHEN,Weilong BAN. Verification technology of multi-model precipitation forecast in Liaoning province in summer 2020 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(6): 37-43. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|