国际刊号:ISSN 1673-503X
国内刊号:CN 21-1531/P

Journal of Meteorology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 65-73.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2023.04.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Shiteng CAO1( ),Lei YANG1,*(
),Lei YANG1,*( ),Yu CHEN1,Li SUN2,Yuxuan LENG3,Chao JIANG1,Xue YANG1
),Yu CHEN1,Li SUN2,Yuxuan LENG3,Chao JIANG1,Xue YANG1
Received:2022-08-19
Online:2023-08-28
Published:2023-09-23
Contact:
Lei YANG
E-mail:957858010@qq.com;yanglei_nuist@163.com
CLC Number:
Shiteng CAO, Lei YANG, Yu CHEN, Li SUN, Yuxuan LENG, Chao JIANG, Xue YANG. Characteristics of spatio-temporal distribution and environmental parameters of Cold Vortex thunderstorm gales in Liaoning province from 2017 to 2021[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(4): 65-73.
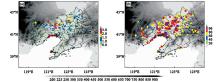
Fig.1
Spatial distributions of the annual average occurrence times of Cold Vortex thunderstorms and gales (a) and the percentage of thunderstorms and gales under the influence of Cold Vortex against the annual average occurrence times (b) convective available potential energy in Liaoning province from 2017 to 2021"
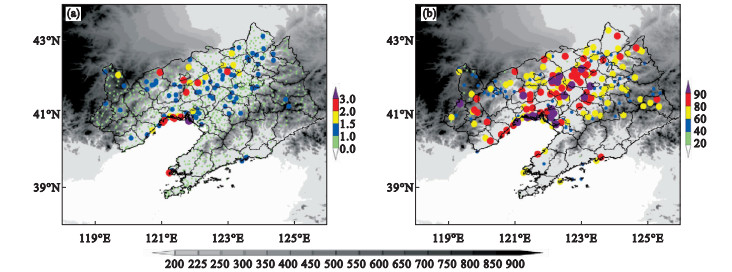
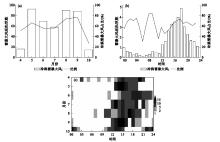
Fig.2
The monthly (a) and diurnal (b) variations of the mean number of stations where thunderstorms and strong winds caused by northeast Cold Vortex occur, and the percentage of the total number of stations where thunderstorms and strong winds occur in each hour in different months against those where thunderstorms and strong winds occur in the month (c) in Liaoning province from 2017 to 2021"
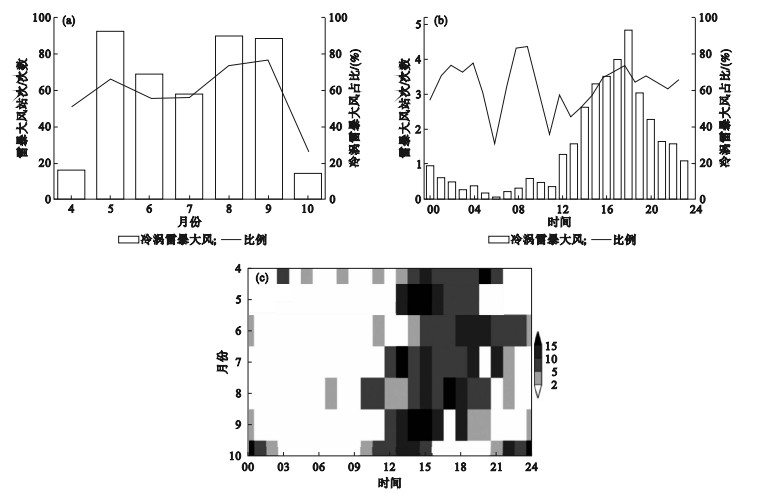
Fig.4
Monthly variations of the temperature difference between 850 hPa and 500 hPa (a), between the ground and 500 hPa (b) and the convective effective potential energy (c) when thunderstorms and strong winds occur under the backgrounds of Cold Vortex and Non-Cold Vortex in Liaoning province from 2017 to 2021"
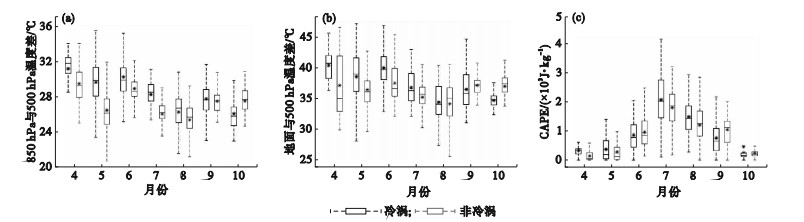
Fig.6
Monthly variations of the lowest relative humidity of 500~400 hPa (a), near ground to 850 hPa (b), the characteristic values of DCAPE (c) and the wind speed of the storm-bearing layer (d) when thunderstorm gales occur under the backgrounds of Cold Vortex and Non-Cold Vortex in Liaoning province from 2017 to 2021"
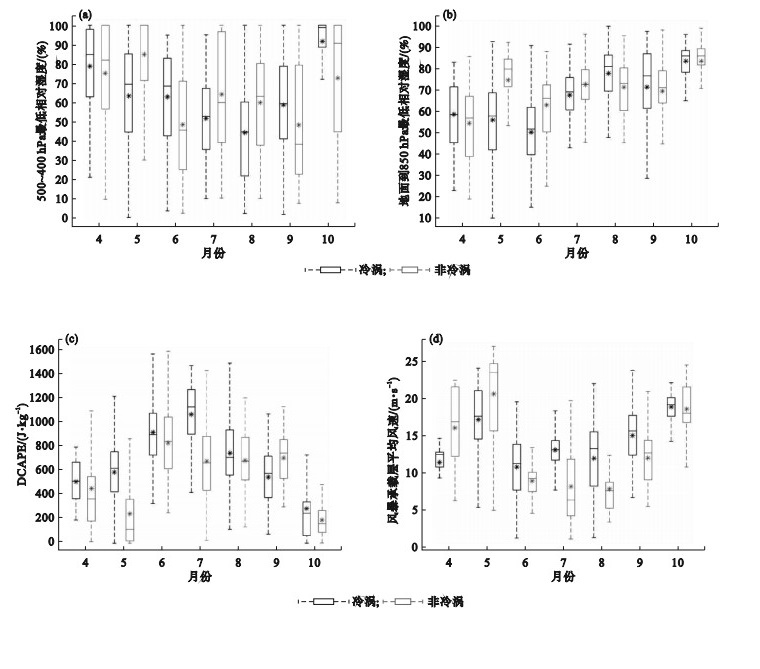
Table 2
Characteristic values of environmental physical quantities when thunderstorms and strong winds occur in the southwest and southeast quadrants of the Northeast Cold Vortex in Liaoning province from 2017 to 2021"
| 物理量 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 25%分位点 | 75%分位点 | |||||||
| 东南 | 西南 | 东南 | 西南 | 东南 | 西南 | 东南 | 西南 | ||||
| PWV/mm | 33.6 | 31.7 | 31.7 | 31.1 | 24.1 | 15.4 | 41.6 | 41.5 | |||
| 850~700 hPa最大相对湿度/(%) | 78.8 | 78.1 | 80.4 | 75.7 | 69.1 | 68.9 | 89.9 | 87.1 | |||
| 地面与500 hPa温度差/℃ | 36.8 | 38.1 | 36.6 | 38.8 | 34.1 | 35.4 | 39.3 | 41.2 | |||
| 850 hPa与500 hPa温度差/℃ | 28.5 | 28.0 | 28.2 | 28.5 | 26.8 | 26.2 | 29.9 | 29.7 | |||
| CAPE/(J·kg-1) | 1041.8 | 778.8 | 811.6 | 530.5 | 337.6 | 97.3 | 1537.8 | 1382.5 | |||
| 500~400 hPa最低相对湿度/(%) | 59.7 | 42.5 | 60.1 | 38.6 | 41.3 | 14.7 | 81.1 | 67.0 | |||
| 850 hPa以下最低相对湿度/(%) | 67.1 | 54.0 | 69.4 | 47.6 | 56.8 | 37.2 | 80.6 | 70.1 | |||
| DCAPE/(J·kg-1) | 726.7 | 765.2 | 694.6 | 715.7 | 501.3 | 618.9 | 947.2 | 895.2 | |||
| 0~1 km风矢量差/(m·s-1) | 8.8 | 6.5 | 8.4 | 6.5 | 5.7 | 3.3 | 11.3 | 9.2 | |||
| 0~6 km风矢量差/(m·s-1) | 17.7 | 17.6 | 17.2 | 16.8 | 14.0 | 12.2 | 20.9 | 22.3 | |||
| 925~500 hPa平均风/(m·s-1) | 14.1 | 12.4 | 13.7 | 14.1 | 11.7 | 7.5 | 17.2 | 16.3 | |||
| 1 | 俞小鼎,郑永光.中国当代强对流天气研究与业务进展[J].气象学报,2020,78(3):391-418. |
| 2 | 王秀明,周小刚,俞小鼎.雷暴大风环境特征及其对风暴结构影响的对比研究[J].气象学报,2013,71(5):839-852. |
| 3 |
费海燕,王秀明,周小刚,等.中国强雷暴大风的气候特征和环境参数分析[J].气象,2016,42(12):1513-1521.
doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.12.009 |
| 4 |
YangX L,SunJ H,ZhengY G.A 5-yr climatology of severe convective wind events over China[J].Weather and Forecasting,2017,32(4):1289-1299.
doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-16-0101.1 |
| 5 | 马淑萍,王秀明,俞小鼎.极端雷暴大风的环境参量特征[J].应用气象学报,2019,30(3):292-301. |
| 6 | 蔡雪薇,谌芸,沈新勇,等.冷涡背景下不同类型强对流天气的成因对比分析[J].气象,2019,45(5):621-631. |
| 7 | 许长义,章丽娜,肖现,等.冷涡背景下华北平原一次弓形回波致灾大风过程分析[J].气象学报,2023,81(1):40-57. |
| 8 | 郑永光,宋敏敏.冷涡影响中国对流性大风与冰雹的分布特征[J].热带气象学报,2021,37(5):710-720. |
| 9 |
JohnsR H,DoswellⅢ C A.Severe local storms forecasting[J].Weather and Forecasting,1992,7(4):588-612.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0434(1992)007<0588:SLSF>2.0.CO;2 |
| 10 |
ConiglioM C,StensrudD J.Interpreting the climatology of Derechos[J].Weather and Forecasting,2004,19(3):595-605.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0434(2004)019<0595:ITCOD>2.0.CO;2 |
| 11 | ConiglioM C,StensrudD J,RichmanM B.An observational study of Derecho-producing convective systems[J].Weather and Forecasting,2004,19(2):320-327. |
| 12 | 孙继松,戴建华,何立富,等.强对流天气预报的基本原理与技术方法—中国强对流天气预报手册[M].北京:气象出版社,2014:13-58, 52-58. |
| 13 | 许爱华,孙继松,许东蓓,等.中国中东部强对流天气的天气形势分类和基本要素配置特征[J].气象,2014,40(4):400-411. |
| 14 | 俞小鼎,王秀明,李万莉,等.雷暴与强对流临近预报[M].北京:气象出版社,2020:135. |
| 15 | MecikalskiJ R,BedkaK M.Forecasting convective initiation by monitoring the evolution of moving cumulus in daytime GOES imagery[J].Monthly Weather Review,2006,134(1):49-78. |
| 16 | 郑永光,陈炯,朱佩君.中国及周边地区夏季中尺度对流系统分布及其日变化特征[J].科学通报,2008,53(4):471-481. |
| 17 | 孙力,郑秀雅,王琪.东北冷涡的时空分布特征及其与东亚大型环流系统之间的关系[J].应用气象学报,1994,5(3):297-303. |
| 18 | 李燕,赛瀚,刘静,等.辽宁省短时强降水气候特征分析[J].气象与环境学报,2017,33(4):56-63. |
| 19 | 陈传雷,杨青,孙欣,等.辽宁省区域性大暴雨特征及预报技术[M].沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社,2019:1-13. |
| 20 | 曹云昌,方宗义,夏青.GPS遥感的大气可降水量与局地降水关系的初步分析[J].应用气象学报,2005,16(1):54-59. |
| 21 | 李崇,吉曹翔,夏传栋,等.沈阳地区强对流天气潜势预报环境参数特征分析[J].气象与环境学报,2016,32(6):43-51. |
| 22 | 杨磊,蒋大凯,王瀛,等.辽宁省汛期GPS遥感大气可降水量的特征分析[J].干旱气象,2016,34(1):82-87. |
| 23 | 高晓梅,俞小鼎,王令军,等.鲁中地区分类强对流天气环境参量特征分析[J].气象学报,2018,76(2):196-212. |
| 24 | 王秀明,俞小鼎,朱禾.NCEP再分析资料在强对流环境分析中的应用[J].应用气象学报,2012,23(2):139-146. |
| 25 | MarkowskiP,RichardsonY.Mesoscale meteorology in midlatitutes[M].Chichester, West Sussex, UK:Wiley-Blackwell Publication,2010:27-31. |
| 26 | 袁潮,李得勤,杨磊,等.冷涡背景下一次微型超级单体龙卷的雷达特征和物理过程探究[J].气象学报,2022,80(6):878-895. |
| 27 | 赵秀英,彭治班,吴宝俊,等.下沉对流有效位能[J].气象,2000,26(6):1-2. |
| 28 | 阎琦,李爽,陆井龙,等.1979—2019年持续性东北冷涡过程特征分析[J].气象与环境学报,2022,38(2):40-45. |
| 29 | 杨珊珊,谌芸,李晟祺,等.冷涡背景下飑线过程统计分析[J].气象,2016,42(9):1079-1089. |
| 30 | 罗琪,郑永光,陈敏.2017年北京北部一次罕见强弓状飑线过程演变和机理[J].气象学报,2019,77(3):371-386. |
| 31 | PaceyG P,SchultzD M,Garcia-carrerasL.Severe convective windstorms in Europe: Climatology, preconvective environments, and convective mode[J].Weather and Forecasting,2021,36(1):237-252. |
| [1] | ZHAO Tingting, MENG Xin, GAO Lingfeng, ZHOU Zewen, LIU Hailong, GAO Jing. Diagnosis and analysis of the extreme blizzard in Liaoning province from 6 to 9,November,2021 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(6): 10-17. |
| [2] | Pengyu HU,Shuang XU,Shibo GENG,Chuanlei CHEN,Chang SU,Shengyuan CHEN. Characteristic analysis of thunderstorm gale process in Shenyang under a background of cold vortex [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(5): 9-18. |
| [3] | Chen XIN, Liangbo QI, Hai CHU. Analysis of the midsummer local convection distribution and weather factors under the control of the Western Pacific subtropical high in the Yangtze Delta region of China [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(4): 57-64. |
| [4] | Yu CHEN, Shi-teng CAO, Chuan-lei CHEN, Ying WANG, Yei YANG, Chao YUAN, Xue YANG, Chao JIANG, Qi-lin ZHANG, Man-li WU. Analysis of the formation and evolution of super tornado occurred in Kaiyuan of Liaoning province on July 3, 2019 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2023, 39(2): 11-19. |
| [5] | Liang-peng DONG,Ping-ping ZHANG. Comparison of abnormalism of meteorological factors on two extreme precipitations triggered by low vortex in Hubei province in 2020 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(6): 20-28. |
| [6] | Li REN, Chen LUAN, Xiao-xue WANG, Yue ZHANG. Causes and characteristics of a persistent rainstorm event in warm front of a cold vortex [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(3): 37-44. |
| [7] | Qi YAN, Shuang LI, Jing-long LU, Fang-da TENG. Characteristics of the continuous cold vortex over Northeast China from 1979 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2022, 38(2): 40-45. |
| [8] | Xu ZHANG,Bao-li SUN,Jia-ning BAI,Dan-mei ZHANG,Ke SUN,Xiao-tong YANG,Zhen-yu ZHAO,Xi-long NING. Evaluation of multi-model precipitation forecast of Northeast Cold Vortex in Fuxin [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2021, 37(3): 19-24. |
| [9] | Duan-yu ZHANG, Fei-yang WANG, Jin-tao YE. Characteristics of rainstorms in central Huanghuai area influenced by a landing tropical cyclone "Rumbia" in 2018 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2020, 36(6): 10-20. |
| [10] | XU Lu-lu, LI Qian, LI Hui-lin, HAN Mei, LUO Jian-yu, MENG Xin. Multi-scale comparative analysis of two hail events in Dandong in September 2018 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(6): 1-7. |
| [11] | YAO Jing, JING Yu, LIU Yong, ZHAO Qiang, WANG Nan. Analyses of the mechanisms of the first regional snowstorm associated with an “Elevated Thunderstorm” over Shaanxi province in 2016 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(6): 24-32. |
| [12] | SHEN Yang, SHEN An-yun, SU Hang, XIONG Shi-wei, YAN Wen-lian. Causes analysis on a large-range dense fog event in the winter of 2016 over Jiangsu province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(4): 11-20. |
| [13] | XIAO Liu-si, CHEN Zhi-gang, HU Dong-ming, LIAO Fei. Characteristic analysis of a tornado developing from the super-typhoon “Mujigae” [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2017, 33(3): 21-28. |
| [14] | LI Ji, JIAO Min, HU Chun-li, LI Fei, ZHANG Xiao-yue, ZHANG Qi, WANG Ying, ZHU Xin-yu. Characteristics of summer temperature and its impact factors in Northeast China from 1951 to 2012 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(5): 74-83. |
| [15] | LIANG Wei-liang, QU Mei-fang, LAI Zhen-quan, NONG Meng-song. Analysis of radar features and environmental background during a severe thunderstorm in early summer 2014 in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(3): 10-18. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|